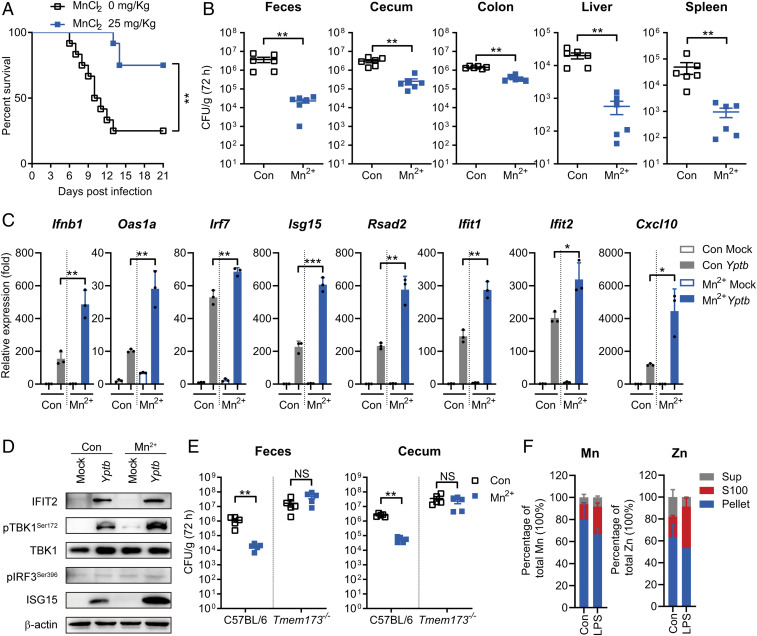
Fig. 4.
Mn2+ primes the antimicrobial immune response via STING. (A and B) C57BL/6 mice were pretreated with or without MnCl2 (25 mg ⋅ kg−1) intraperitoneally for 24 h and were intragastrically inoculated with Yptb WT. (A) The survival rate of the mice was determined. (B) Homogenates of different tissues were plated to determine the bacterial CFU counts per gram in the indicated organs of the untreated (Con) or Mn2+-treated (Mn2+) mice at 72 h postinfection. (C and D) qRT-PCR analysis of the gene expression (C) and immunoblot analysis of the protein (D) in PMs untreated (Con) or pretreated with 100 μM MnCl2 (Mn2+) for 24 h and mock infected (Mock) or infected with Yptb WT. (E) C57BL/6 or Tmem173−/− mice were untreated (Con) or pretreated with MnCl2 (25 mg ⋅ kg−1) (Mn2+) intravenously for 24 h and intragastrically inoculated with Yptb WT. Homogenates of feces and cecum were plated to determine the bacterial CFU numbers per gram of organs at 72 h postinfection. (F) Mn and Zn concentrations in the indicated cellular components and culture medium (Sup). Raw264.7 cells were untreated (Con) or treated with LPS (4 μg ⋅ mL−1). Data in C were normalized to untreated, mock-infected control (Con Mock, set as 1). Gapdh was used as the housekeeping gene. Error bars represent ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; NS, not significant.