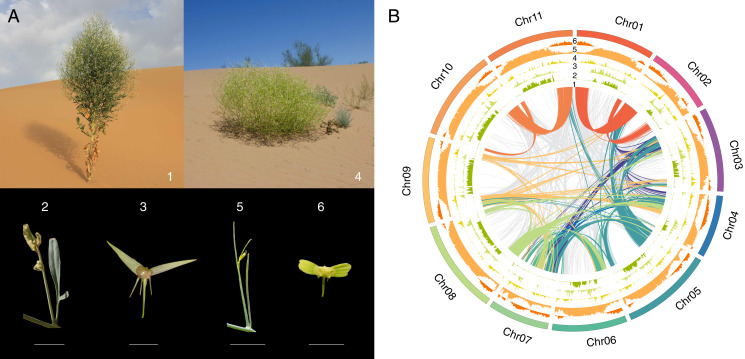
Fig. 1.
The contrasted habit and morphology of the two Pugionium species and genomic structure of P. cornutum. (A) Morphological and habitat divergence of the two species (1, 2, and 3 for P. cornutum and 4, 5, and 6 for P. dolabratum) on the basal branching and stem height, leaf (lobe width), silique morphology (valve and wing length and angle ), and habitat (mobile and fixed dunes). (Scale bar: 1 cm.) (B) Collinearity within the P. cornutum genome. Color-coded lines in the middle (1) show gene synteny between chromosomes. Histograms from inside to outside show frequencies of tandem repeats (2), LTR/Gypsy retrotransposons (3), LTR/Copia retrotransposons (4), overall repetitive contents (5), and densities of genes (6), respectively.