Figure 4.
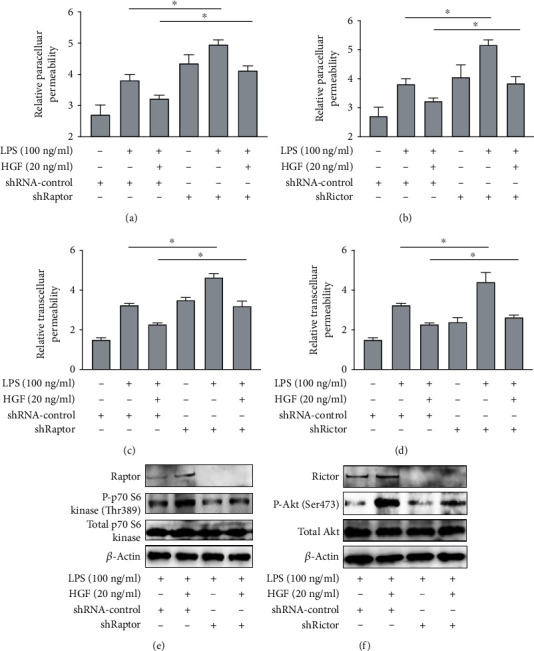
Effects of mTORC1 and mTORC2 to HGF on endothelial permeability in LPS-induced PMVECs. Lentivirus vector-mediated mTORC1 (raptor) and mTORC2 (rictor) knockdown in PMVECs (shRaptor and shRictor as knockdown, shRNA-control as negative control) was conducted. PMVECs were treated with HGF (20 ng/ml), with or without stimulation with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. (a) The effects of mTORC1 to relative paracellular permeability of HGF on LPS-induced PMVEC permeability with Alexa Fluor 647-dextran. (b) The effects of mTORC2 to relative paracellular permeability of HGF on LPS-induced PMVEC permeability with Alexa Fluor 647-dextran. (c) The effects of mTORC1 to relative transcellular permeability of HGF on LPS-induced PMVEC permeability with Alexa Fluor 647-BSA. (d) The effects of mTORC2 to relative transcellular permeability of HGF on LPS-induced PMVEC permeability with Alexa Fluor 647-BSA. (e) Evaluation of HGF on mTORC1 signaling pathway for western blot. (f) Evaluation of HGF on mTORC2 signaling pathway for western blot. Results are mean ± SD (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05.
