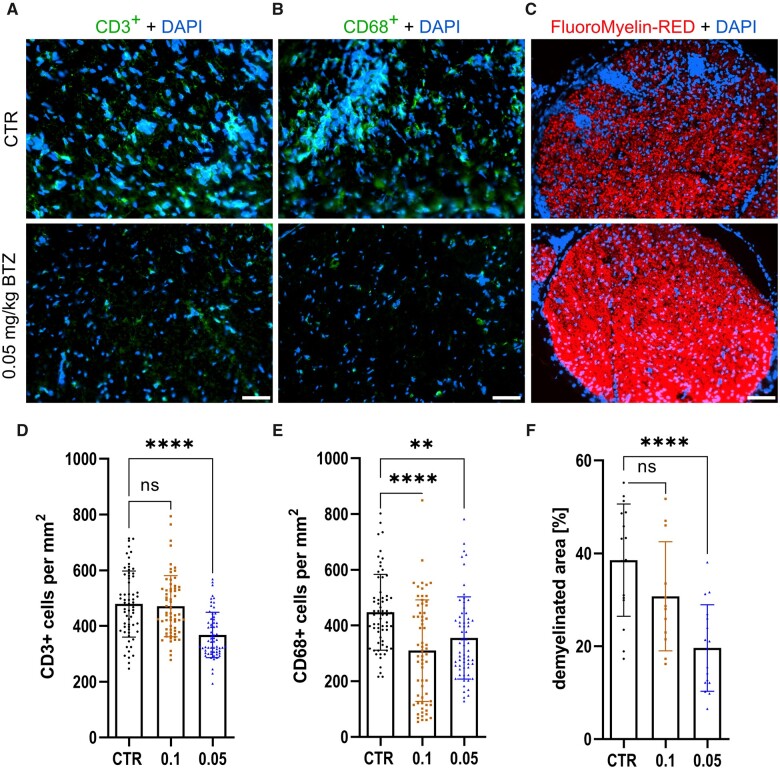
Figure 7.
Low dose BTZ treatment reduced inflammation and demyelination in the sciatic nerve. Representative pictures of CD3, shown in A, CD68, shown in B, and FluoroMyelin™-Red, shown in C, staining of the sciatic nerve. Treatment with 0.05 mg/kg BTZ significantly reduced infiltration of CD3+ T cells, shown in D (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test, P-value < 0.0001, statistical analysis for N 0 64 technical replicates) and demyelination of the sciatic nerve, shown in F (one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test, P-value < 0.0001, statistical analysis for n = 16 technical replicates). In addition, 0.05 as well as 0.1 mg/kg BTZ significantly reduced infiltration of CD68+ cells into the sciatic nerve, shown in E [Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test, P-value < 0.0001 (CTR versus 0.1) and P-value = 0.0012 (CTR versus 0.05); statistical analysis for n = 64 technical replicates]. The experiment was performed three times. D, E and F show the results of one representative experiment, therefore each data point represents a technical replication. Scale bar: 50 µm.