Figure 5.
High-throughput structural analysis of integral membrane proteins ADIPOR2 and ACER3
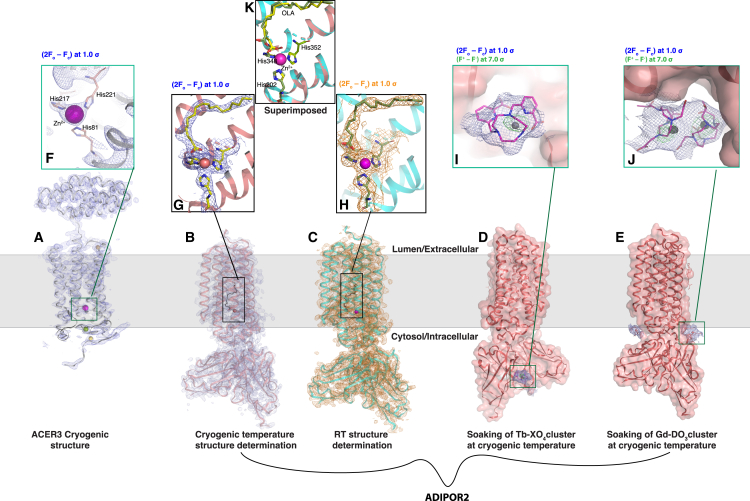
Structures of the ACER3 and ADIPOR2 seven-transmembrane enzyme receptors were obtained with the workflows presented in Figure 1. Protein crystal structures are shown with the membrane plane indicated as a gray zone.
(A–C) (A) ACER3 cryogenic structure, shown as a cartoon in gray and (2Fo − Fc) map in blue; (B) ADIPOR2-scFv cryogenic structure, shown as cartoon in salmon with (2Fo − Fc) map; and (C) ADIPOR2-scFv room-temperature (RT) structure, shown as cyan cartoon with orange (2Fo − Fc) map.
(D and E) ADIPOR2-scFv structures shown as surface structures, highlighting (D) Tb complex and (E) Gd complex as soaked clusters with (2Fo − Fc) map in blue. All (2Fo − Fc) maps are contoured at 1.0 σ.
(F–H) Inset views of active sites of (A), (B), and (C), respectively, showing Zn2+ atoms as magenta spheres, coordinated by His residues shown as sticks, with the respective (2Fo − Fc) maps, matching the color.
(I and J) Inset views of the (I) Tb complex and (J) Gd complex, shown in magenta sticks with metal atoms shown as gray spheres, along with the (2Fo − Fc) map in blue and anomalous maps in green (contoured at 7.0 σ). PDB codes are ACER3 cryo: 6YXH; ADIPOR2 cryo: 6YX9; ADIPOR2 RT: 6YXD; ADIPOR2-Tb-XO4: 6YXG; ADIPOR2-Gd-DO3: 6YXF.
(K) Superposition showing distinct conformations of the oleic acid molecule at the catalytic site of ADIPOR2 in the cryogenic (green) and room-temperature structures (yellow).