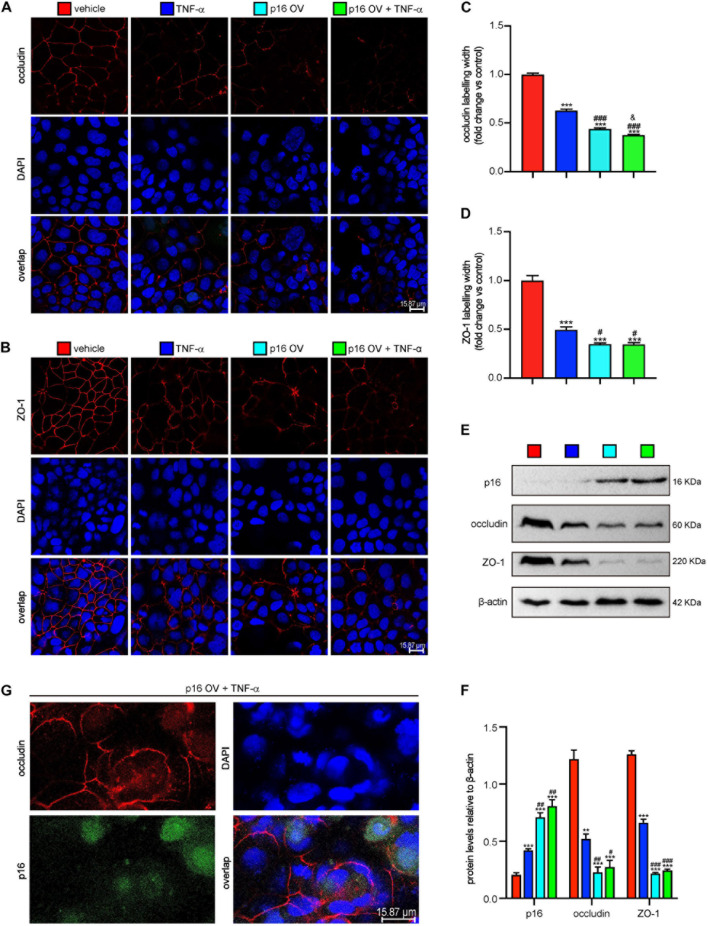
FIGURE 4.
Accumulated p16 in Cacao-2 cells blocked the repair of TJ after TJ was damaged by TNF-α. The Cacao-2 cells were transfected with GFP-labeled Flag-p16–overexpressed (p16-OV) or vehicle adenovirus and then treated with or without 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 24 h. Immunofluorescence staining was introduced to detect the expressions of occludin and ZO-1. (A) Representative micrographs showing immunofluorescence for occludin, with DAPI staining the nuclei. (B) Representative micrographs showing immunofluorescence for ZO-1, with DAPI staining the nuclei. (C) Occludin positive width relative to control group. (D) ZO-1 positive width relative to control group. (E) Western blots for p16, occludin, and ZO-1 in Cacao-2 cells, and β-actin was used as the loading control. (F) Protein levels relative to β-actin were assessed by densitometric analysis. Cell experiments were performed with three biological repetitions per group. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA test. Values are mean ± SEM from six determinations per group, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared with the vehicle group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared with TNF-α–treated group, &P < 0.05 compared with the p16-OV group. (G) Representative micrographs showing occludin and GFP-labeled p16 in p16-OV and TNF-α–treated cells, with DAPI staining the nuclei.