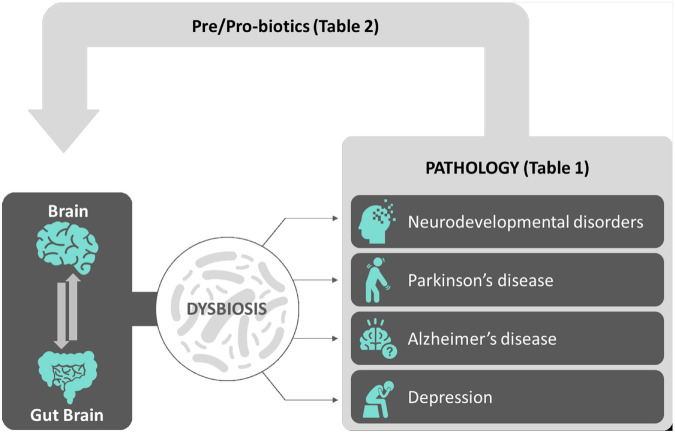
FIGURE 1.
Sketch depicting an overview of the review. The complex interactions between the brain and the gut–brain (gut microbiota) contribute to the physiological balance achieved during normal brain functions. Alterations of gut microbiota microflora leading to gut dysbiosis have been correlated to a number of brain conditions including neurodevelopmental disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and depression, described both in animal models and in mankind (see Table 1 for a summary). Among possible effective new therapeutic avenues, pre/probiotic supplements aimed to correct gut microflora dysbiosis and to reinstate neurophysiological balance in neuropathological background had been shown so far to be effective in a number of clinical trials (see Table 2 for a summary).