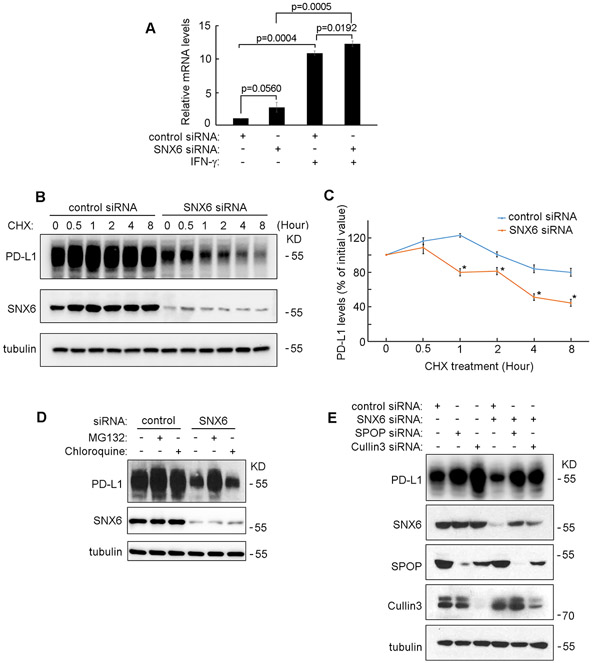
Figure 2. SNX6 modulates the protein degradation of PD-L1.
(A) Control siRNA or SNX6 siRNA was transfected into UMSCC1 cells. 48 hours after siRNAs transfection, the cell were treated with or without IFNγ (100 ng/ml) for 12 hours and the PD-L1 mRNA levels in these cells were quantified by Real-Time PCR. (B) UMSCC22B cells were transfected with control or SNX6 siRNA, the cells were then treated with CHX (50 μg/ml) CHX for the indicated times. Then the levels of PD-L1 and SNX6 were detected by western Blot. Levels of tubulin were used as loading control. (C) Quantification of PD-L1 levels in control or SNX6-knockdown UMSCC22B cells treated with CHX (relative to time point 0). (D) UMSCC22B cells were transfected with control or SNX6 siRNA, and then treated with proteasome inhibitor MG132 (50 μM) or lysosome inhibitor chloroquine (80 μM) for 6 hours. The PD-L1 and SNX6 protein levels were then detected by Western Blot. (E) SPOP siRNA or Cullin3 siRNA was transfected alone or co-transfected with SNX6 siRNA into UMSCC22B cells as indicated. 72 hours after siRNAs transfection, the PD-L1, SNX6, SPOP, and Cullin3 expression levels were detected by Western Blot. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05.