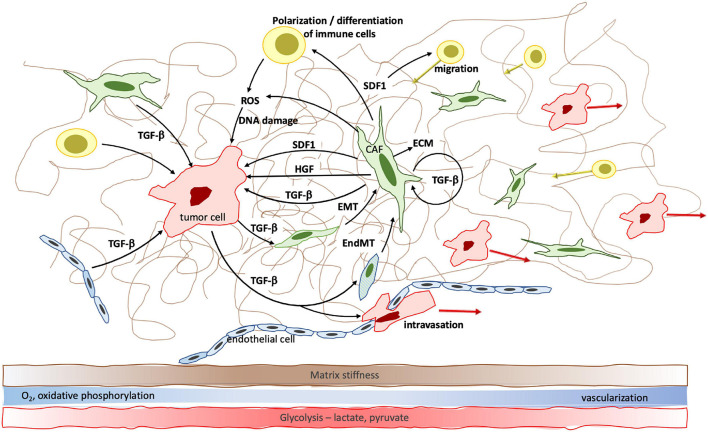
FIGURE 2.
TGF-β facilitates cell-cell communication within the tumor microenvironment and changes cell differentiation, polarization and metabolism to promote tumor growth. Specifically, TGF-β induces fibroblast—myofibroblast transition, epithelial—mesenchymal transition (EMT) and endothelial—mesenchymal transition (EndMT) which result in increased cancer associated fibroblast (CAF) density. CAFs significantly contribute to increased matrix stiffness. EndMT furthermore leads to reduced endothelial cell-cell contacts which facilitates transmigration of tumor cells and metastatic spread. The effect of TGF-β on cell metabolism leads to a shift from oxidative phosphorylation to anaerobic glycolysis and accumulation of lactate, pyruvate and genome-damaging ROS in the hypoxic tumor center.