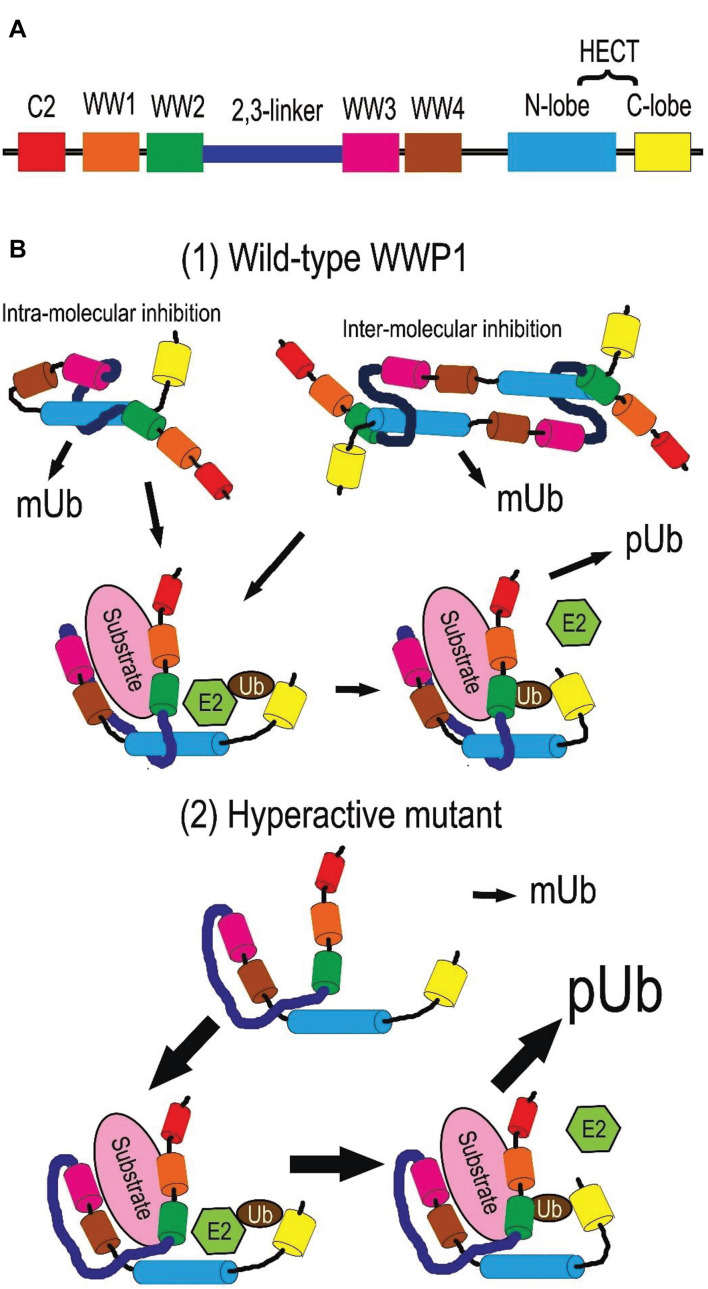
FIGURE 2.
Protein structure and activity regulation of WWP1. (A) Depiction of WWP1 protein structure. Each domain is depicted in a certain color (the same below). (B) Activity regulation of WWP1. (1) Wild-type WWP1 is autoinhibited via intra- or inter-molecular interactions in a steady state: the HECT domain is sequestered by the 2,3-linker and WW2∼4 domains. In this state, WWP1 has the monoubiquitination (mUb) activity to modify itself and some substrates. Binding of a substrate can partially disrupt the inhibitory interactions and release WW domains from N-lobe. This endows WWP1 with moderate polyubiquitination (pUb) activities: the N- and C-lobes collaborate to transfer ubiquitin chains (Ub) from E2 ligases sequentially. (2) Some cancer-related mutations severely break the autoinhibitory interactions and generate hyperactive WWP1 proteins, which induce elevated polyubiquitination of some substrates.