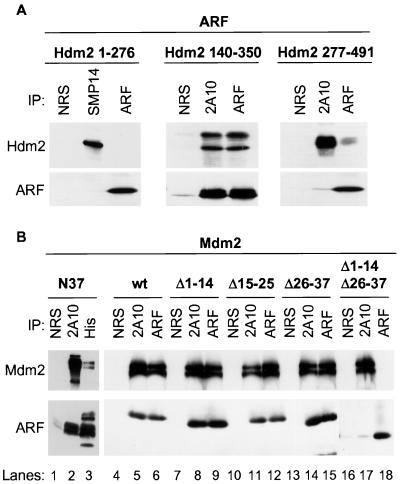
FIG. 3.
Two domains within the N terminus of mouse ARF and a central region of Mdm2 or Hdm2 are required to form the ARF-Mdm2 complex. (A) Polyhistidine-tagged Hdm2 proteins isolated from bacteria by nickel affinity chromatography were mixed for 1 h at 4°C with recombinant ARF protein prepared in baculovirus vector-infected insect Sf9 cells. Hdm2 and ARF proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with monoclonal antibodies to Hdm2 (SMP14 or 2A10 as indicated) or with antibody directed to the p19ARF C terminus (ARF) compared with precipitation with NRS. Precipitated proteins electrophoretically separated on denaturing gels were transferred to filters and immunoblotted with the same antibodies. (B) Polyhistidine-tagged syn-ARF N37 was mixed for 1 h at 4°C with recombinant Mdm2 produced in insect Sf9 cells (left). Sf9 cells were coinfected with baculoviruses encoding Mdm2 and the indicated ARF mutants. Mdm2 and ARF proteins were precipitated with 2A10 antibody to Mdm2 or with antibody to the ARF C terminus, whereas syn-ARF N37 was recovered using antibody to polyhistidine compared with NRS. The separated proteins were immunoblotted with the same antibodies.