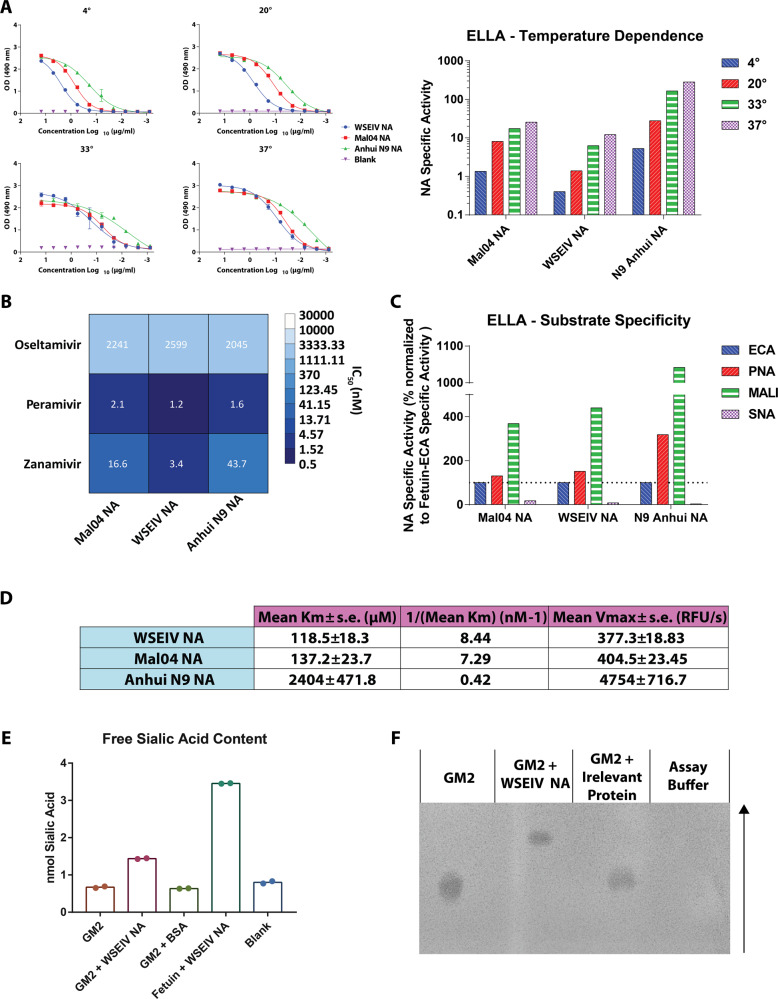
Fig. 3. Functionally, the WSEIV NA is strikingly similar to the influenza B/Malaysia/2506/2004 virus NA.
A Sialidase activity of recombinant WSEIV, influenza B/Malaysia/2506/2004 and A/Anhui/1/2013 H7N9 NA proteins was evaluated in an enzyme-linked lectin assay using fetuin, at four temperatures; 4, 20, 33, 37 °C. The curves indicate absorbance measured at 490 nm with error bars indicating standard deviation. Specific enzyme activity (inverse of half-maximum lectin binding) determined by these absorbance curves are shown for each individual NA at each temperature. B Susceptibility to NA inhibitors was tested in an ELLA-based neuraminidase inhibition assay . Error bars indicate standard deviation. Absorbance at 490 nm based on lectin binding was measured with increasing concentrations of oseltamivir, peramivir or zanamivir. C Neuraminidase substrate specificity was assessed using an ELLA with fetuin and lectins with different specificities (ECA, PNA, SNA, and MALI). Specific enzyme activity was determined as described in (A) and it is represented as a percentage normalized to fetuin-ECA. D Michaelis–Menten parameters, Vmax and Km, were estimated based on enzymatic activity of recombinant NAs against MUNANA substrate. The A/Anhui/1/2013 N9 NA served as a comparative control for both the WSEIV and B/Malaysia/2506/2004 NAs. E Cleavage of sialic acid on GM2 by the WSEIV NA was confirmed using an assay to measure free sialic acid content (sialic acid NANA assay kit, Abcam). F Thin layer chromatography was used to visualize the presence of cleaved GM2 following treatment with the WSEIV NA. The arrow shows the direction in which the chromatography was run. A representative image is shown after the assay was performed in independent duplicates. Technical duplicates were performed once for (A–E).