Figure 2.
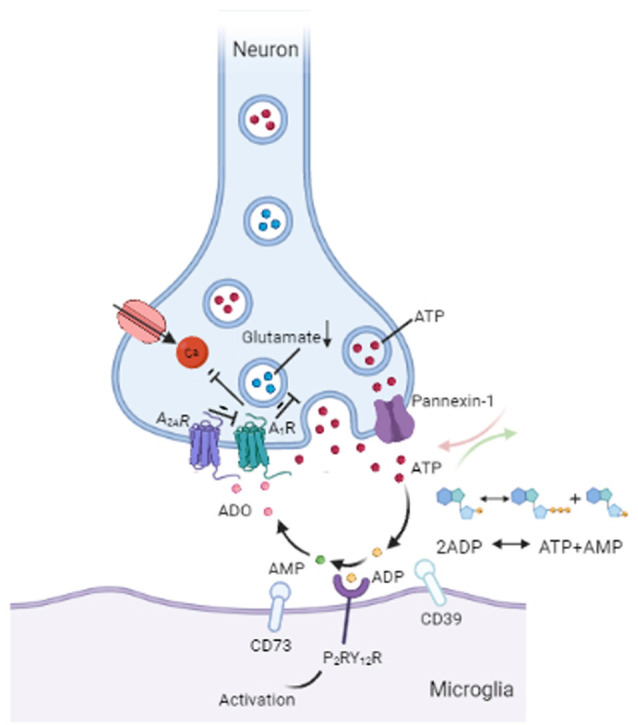
Communication between microglia and neurons. ATP can be secreted from neurons through vesicles or the pannexin-1 channel. Released ATP (red) is converted into ADP (yellow) by the microglial enzyme CD39. ADP acts on P2RY12 receptors to induce activation of P2RY12 signaling, which attracts microglial processes to synaptic connections. CD39 also converts ADP into AMP (green). Next, AMP is converted into ADO (pink) by the enzyme CD73 on microglia. ADO suppresses neuronal activity by acting on A1Rs by decreasing glutamate (blue) release and inhibiting calcium (Ca2+) channels. In addition, A2ARs can weaken the inhibitory effect of A1Rs on glutamate release. ATP = adenosine triphosphate, ADP = adenosine diphosphate, AMP = adenosine monophosphate, ADO = adenosine, A1R = A1 receptor, A2AR = A2A receptor.
