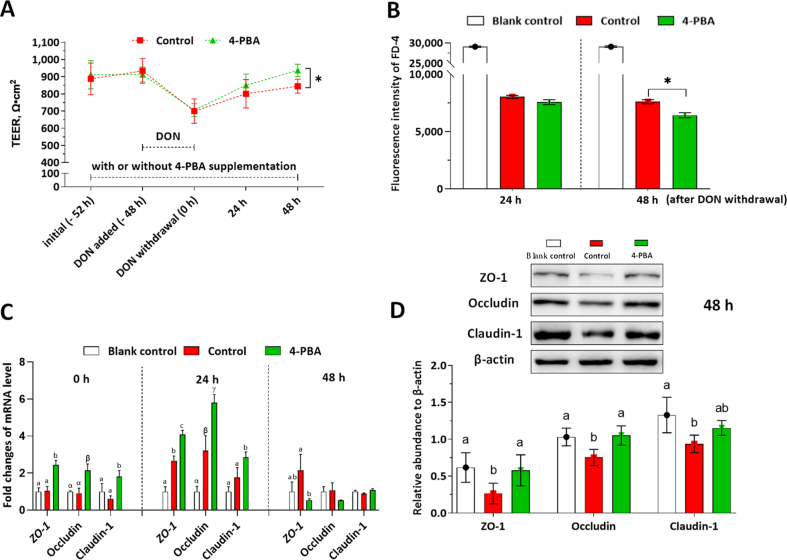
Fig. 4.
Effects of 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) on the intestinal porcine epithelial cell (IPEC)-J2 monolayer during deoxynivalenol (DON)-induced damage and self-rehabilitation. The cell monolayers were treated with or without 1.0 μmol/L 4-PBA (control, 4-PBA group) during all the experimental periods. DON at 2.0 μg/mL was added in the medium at −48 h and withdrawn at 0 h. The positive control (PC) group represents these wells in 6-well trans-well plate without cell seeding. The blank control group represents cell monolayers without any treatment. The transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) measurement and fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran (FD-4) permeability experiments were conducted in 6-well transwell plates. (A) TEER values of the IPEC-J2 monolayers in each group were shown. (B) FD-4 fluorescence intensities of the culture medium in the basal compartment were presented. (C) The relative mRNA levels of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 in each group were presented as the normalized ratio to the blank control. (D) The relative protein levels of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-1 to β-actin were shown. Data were presented as means ± SD, n = 3. Data sets marked with ∗, or different letters represent a significant difference (P < 0.05).