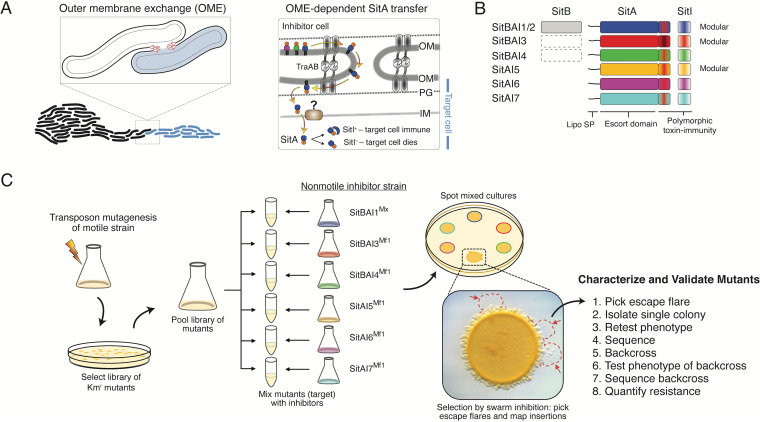
FIG 1.
Model of OME and screening strategy. (A, left) Two myxobacterial swarms initiate contact and OME. (Right) Detailed model of TraAB-mediated OM fusion and SitA lipoprotein translocation. PG, peptidoglycan. (B) Schematic of the six SitAI families. Some families contain the SitB accessory protein, which is encoded immediately upstream of sitA genes (12, 14). The dashed rectangle indicates that sitB is occasionally associated with sitAI loci. (C) Screen schematic. The traAB merodiploid motile strain was mutagenized to create transposon libraries that were pooled, split, and mixed with the indicated nonmotile inhibitor strains with unique sitAI loci. SitA-resistant mutants were identified as escape flares (red arrows) and analyzed. Four to 15 rounds of screening were conducted against each inhibitor strain (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material).