FIG 2.
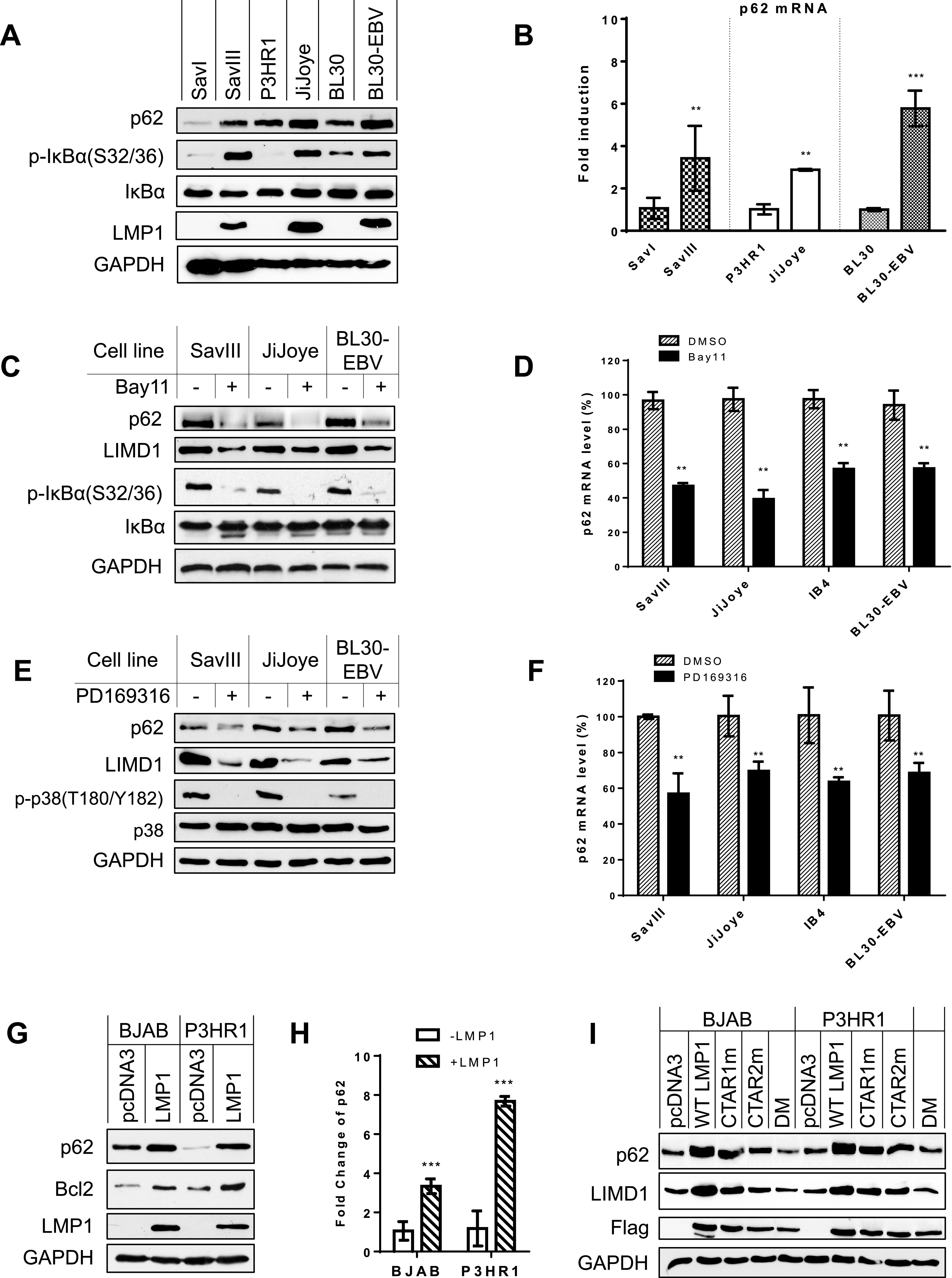
p62 is upregulated by NF-κB and AP1 downstream of LMP1 signaling. (A and B) p62 mRNA and protein expression levels are correlated with NF-κB activity in paired B cell lines. RNA was extracted from indicated different pairs of cell lines, and p62 mRNA expression level was evaluated by real-time qPCR. Consistent results were obtained from at least three independent repeats, and representative results from these consistent repeats are shown. The average mRNA levels of the triplicates in SavI, P3HR1, and CEM were set to 1. (C and D) Inhibition of NF-κB activity in virus-transformed cells downregulates p62 expression. NF-κB activity in type 3 latency cells was inhibited with the NF-κB-specific inhibitor Bay11-7085 at a concentration of 2.5 μM for 48 h. The average mRNA levels of the duplicates in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-treated cells were set to 100%. The p62 mRNA levels decreased by Bay11-7085 treatment are shown as percentages of those with corresponding DMSO controls. (E and F) Inhibition of p38 activity in virus-transformed cells downregulates p62 expression. PD169316 was applied at 5 nM for 48 h. (G and H) LMP1 induces p62 expression. BJAB and P3HR1 stable cell lines expressing Flag-LMP1 or controls were generated by transfecting with pLXCN/Flag-LMP1 expression and control plasmids, selected with 2 mg/ml G418 for 2 weeks, and then subjected to immunoblotting and qPCR analysis. The average mRNA levels of the triplicates in pcDNA3-transfected cells were set to 1. (I) Both LMP1 CTAR1 and -2 contribute to p62 expression. BJAB and P3HR1 cells were transfected with Flag-LMP1 or its point mutants. Cells were collected 48 h post-transfection, followed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. Statistical analysis was performed on results from three independent experiments. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.
