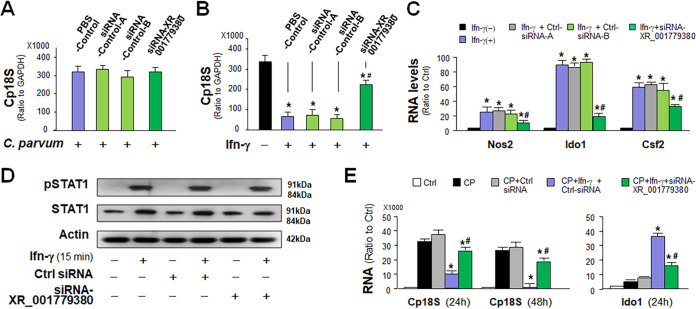
FIG 2.
Upregulation of XR_001779380 promotes IFN-γ-mediated epithelial antimicrobial defense. (A) Impact of siRNA knockdown of XR_001779380 on C. parvum infection burden in intestinal epithelial cells. Knockdown of XR_001779380 in IEC4.1 cells showed no detectable effects on C. parvum infection burden. (B) siRNA knockdown of XR_001779380 on IFN-γ-mediated epithelial anti-C. parvum defense. Pretreatment of IEC4.1 cells with IFN-γ decreased C. parvum infection burden. Treatment of IEC4.1 cells with the siRNA to XR_001779380, but not the nonspecific siRNA controls, attenuated the inhibitory effects of IFN-γ pretreatment on C. parvum infection burden. (C) Knockdown of XR_001779380 attenuated IFN-γ-induced expression of Ido1, Nos1, and Csf2 in IEC4.1 cells as assessed using qRT-PCR. (D) Knockdown of XR_001779380 did not alter Stat1 phosphorylation in IEC4.1 cells induced by IFN-γ. Representative gel images from at least three independent experiments are shown. (E) IFN-γ treatment decreased C. parvum infection burden and induced the expression of Ido1 in enteroids, which are attenuated by siRNA knockdown of XR_001779380. Data are shown as the means ± SD from at least three independent experiments. Statistical significance (ANOVA test): *, P < 0.01 versus noninfection or non-IFN-γ-treated control; #, P < 0.01 versus IFN-γ- and control siRNA-treated group.