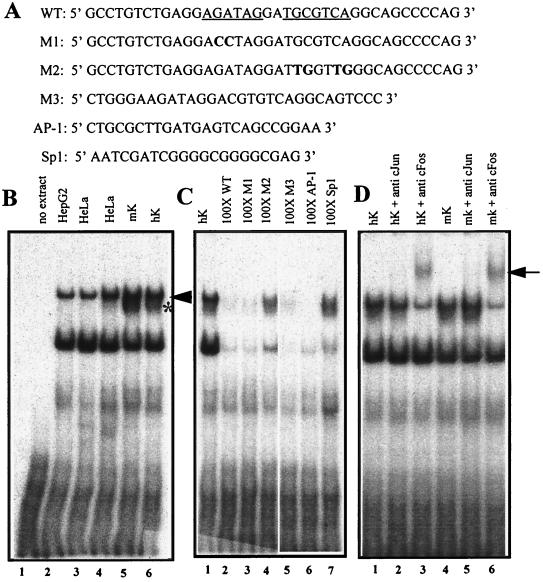
FIG. 6.
EMSAs of nuclear extracts showing binding of AP-1 to a motif within the 125-bp HSsII K14 enhancer. (A) The wild-type oligonucleotide (WT) corresponds to the human sequence and is shown at the top, with the GATA and AP-1 sites underlined. Mutant oligonucleotides are shown below, with mutations in bold. M1, GATA mutant; M2, AP-1 mutant; M3, corresponding WT mouse sequence (Fig. 5B); AP-1 and Sp1 are consensus oligonucleotides for these two transcription factor family members and were purchased from Promega. (B) EMSAs were performed with radiolabeled WT oligonucleotide and nuclear extracts (4 to 6 mg) from the cell type indicated above each lane. Arrowhead and asterisk denote broadly expressed and keratinocyte-specific AP-1 complexes, respectively; note that all complexes within this mobility range were supershifted with AP-1 antibodies (D). (C) EMSAs were performed as for panel B, this time using radiolabeled WT oligonucleotide and a 100-fold excess of the unlabeled double-stranded oligonucleotide indicated above each lane. Note that the AP-1 complexes were specifically competed only by oligonucleotides encompassing an AP-1 binding site, whereas most other complexes were competed nonspecifically with all oligonucleotides. (D) EMSAs were performed as for panel B, but anti-c-Jun and anti-c-Fos were added to the complexes prior to gel electrophoresis. The arrow indicates supershifts, reflective of complexes between AP-1, DNA, and antibody.