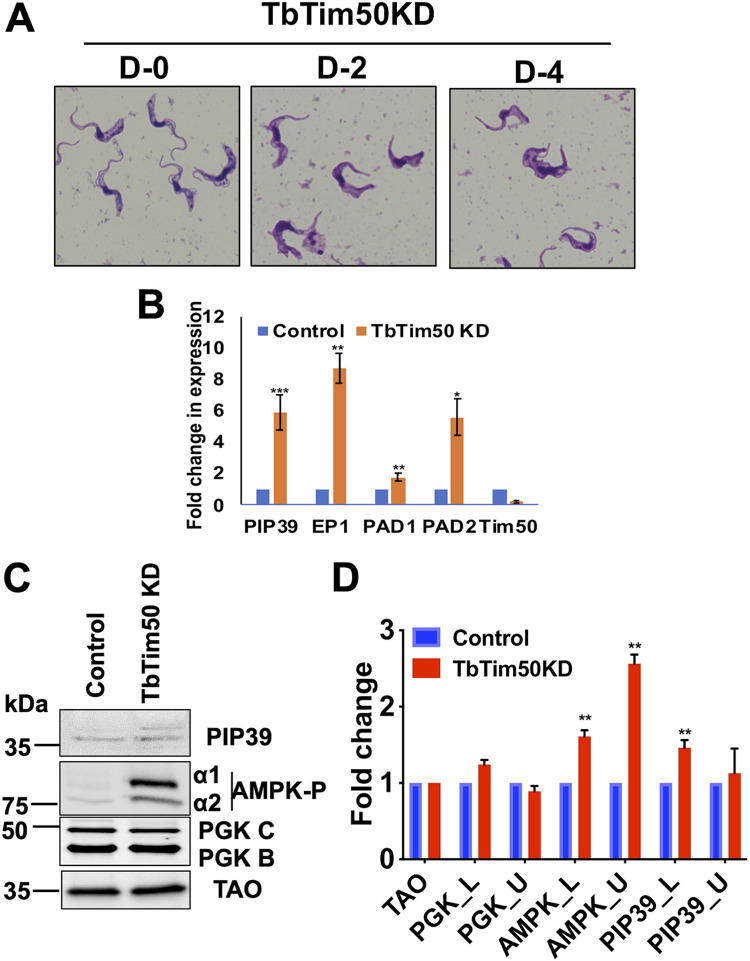
FIG 7.
TbTim50 KD altered cell morphology, increased AMPK phosphorylation, and upregulated expression of the ST-specific transcripts. (A) Giemsa-stained TbTim50 RNAi cells at days 0, 2, and 4 after induction with doxycycline. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the EP1, PAD1, PAD2, PIP39, and TbTim50 transcripts in control and TbTim50 RNAi T. brucei BF cells grown for 2 days in the presence of doxycycline. Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) was used as the internal control. Relative levels of the marker transcripts compared to those in the parental control were plotted. Averages and standard errors were calculated from three experiments. (C) Immunoblot analysis of total proteins from the control and TbTim50 KD cells harvested after 4 days postinduction using different antibodies against PIP39, phospho-AMPK, PGK, and TAO as probes. (D) Densitometric analysis of the protein bands for PIP39_upper (PIP39_U), PIP39_lower (Pip30_L), AMPKα1P, AMPKα2P, PGK_B, and PGK_C after normalization with that for TAO. Values shown are mean fold increase ± standard error in TbTim50 KD in comparison to the control from triplicate experiments. Significance values were calculated by t test and are indicated by asterisks as follows: **, P < 0.05; *** P < 0.01.