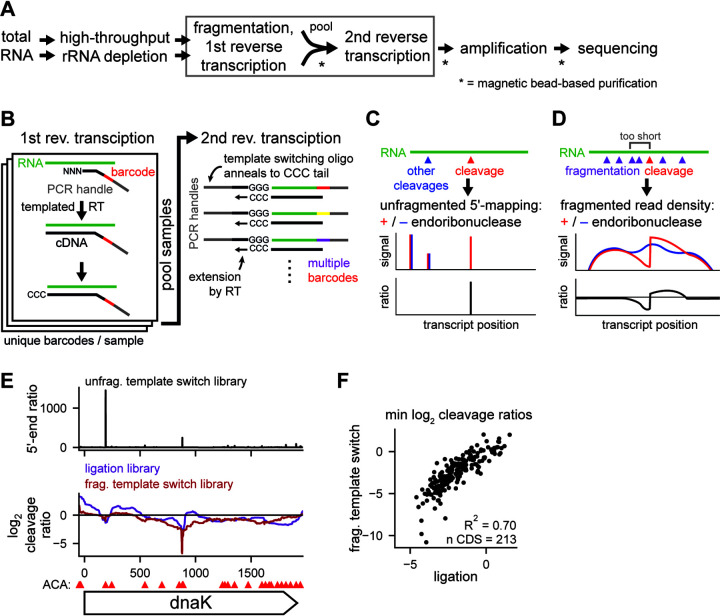
FIG 2.
Using template switch libraries to characterize endoribonuclease cleavage. (A) Workflow for template switching libraries. Steps with multiple arrows between are unpooled, and single-arrow steps are pooled. Steps requiring a purification are starred. Steps shown in panel B are boxed. (B) Cartoon illustrating the molecular details of the first and second reverse transcription steps in panel A. (C) Cartoon illustrating how 5′ ends are mapped at single-nucleotide resolution using template switch libraries. “Cleavage” indicates cleavage by a given toxin; “other cleavages” refers to cleavage by housekeeping and other RNases. (D) Cartoon illustrating how the extent of cleavage is quantified using fragmented template switch libraries. (E) Mapping of MazF cleavage across the dnaK gene after 5 min of toxin expression. (Top) 5′-end ratios from template switch libraries (geometric mean of 2 replicates). (Middle) Cleavage profiles from fragmented template switching libraries (red; n = 2) and ligation libraries (purple; n = 2). (Bottom) ACA sites within dnaK are shown as red triangles above the gene. (F) Scatterplot comparing coding region minimum cleavage ratios from template switch and ligation libraries within highly expressed coding regions (≥256 reads at all positions in both library types).