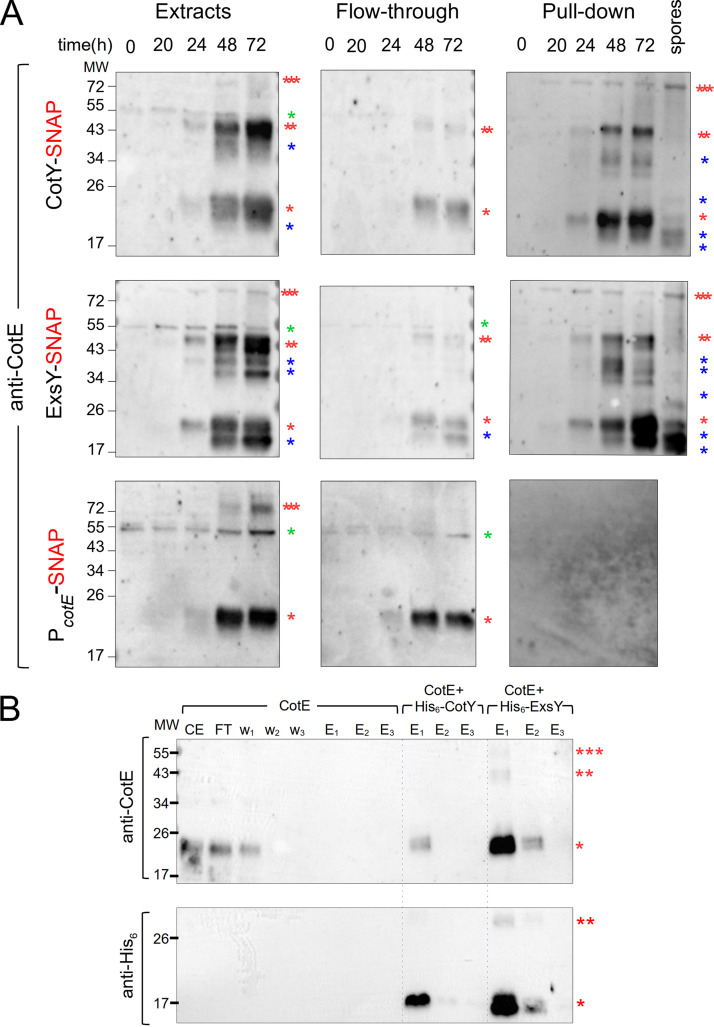
FIG 4.
CotE, CotY, and ExsY form complexes in vivo and interact in vitro. (A) Samples were collected at the indicated times from sporulating cultures of B. cereus strains producing various SNAP fusions. Whole-cell extracts were prepared and subjected to pulldown assays with a SNAP capture resin. Whole-cell extracts, flowthrough, and bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analyses with anti-CotE antibodies. A lane corresponding to a pulldown assay performed on proteins extracted from purified CotY-SNAP and ExsY-SNAP spores was added. One red asterisk indicates a monomer of CotE; two red asterisks, a potential dimer of CotE; three red asterisks, multimers; blue asterisks, possible proteolytic products of CotE. A nonspecific signal in the extracts from vegetative cells (hour 0) is indicated by a green asterisk. (B) Heterologous coexpression pulldown assays. E. coli BL21(DE3) cells either producing CotE alone or coproducing CotE with His6-CotY or His6-ExsY were lysed and subjected to pulldown assays. Proteins were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-CotE (top) or anti-His6 (bottom) antibodies. While CotE produced alone was not eluted from the Ni2+ beads (6th to 8th lanes, top), His6-CotY pulled down CotE in E1 (9th lane, top) and was detected in E1 and E2 (9th and 10th lanes, bottom). CotE was pulled down with His6-ExsY in E1 and E2 (12th and 13th lanes, top) and was detected in E1 and E2 (12th and 13th lanes, bottom). CE, cell extract; FT, flowthrough; w1 to w3, washes; E1 to E3, elutions. Red asterisks indicate the different species of CotE (upper panels), His6-tagged CotY (9th to 11th lanes, bottom), or His6-tagged ExsY (12th to 14th lanes, bottom). The positions of molecular weight (MW) markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left.