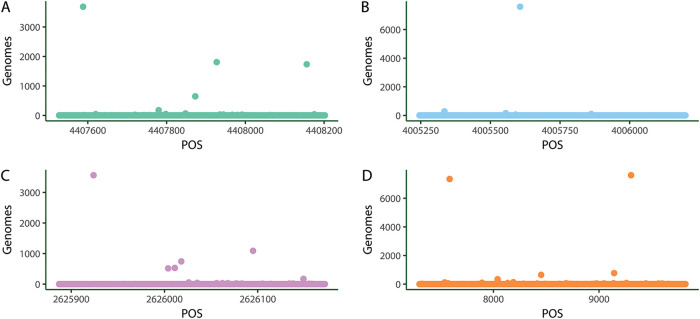
FIG 2.
Variant hot spots within M. tuberculosis genes gidB (A), fadE33 (B), esxO (C), and gyrA (D). Four representative examples of genes with high variation: gidB, a gene associated with streptomycin resistance (6); fadE33 (a member of the fadE family), which plays a role in cholesterol metabolism (25); esxO, which belongs to the ESAT-6 group (16); and gyrA, associated with quinolone drug resistance (6). (A) gidB. The majority of genomic positions (POS) within gidB are conserved. However, 3,690 genomes had a variant at position 4407588, 1,811 genomes had a variant at position 4407927, and 1,734 genomes had a variant at position 4408156. (B) fadE33. The majority of genomic positions within fadE33 are conserved. However, 7,603 genomes had a variant at position 4005607, and 279 genomes had a variant at position 4005335. (C) esxO. The majority of genomic positions within esxO are conserved. Examples of highly variable genomic areas within esxO are positions 2625924 and 2626095. Specifically, 3,561 genomes had a variant at position 2625924 and 1,088 genomes had a variant at position 2626095. (D) gyrA. gyrA, which is associated with drug resistance to quinolones (6), is 2,517 bp (bp) long, and across the analyzed population, the majority of genomic positions within gyrA are conserved. This gene exhibits variation only at certain positions, some of which are known to be associated with quinolone resistance (e.g., 7,345 genomes had a variant at position 7585). In addition, 7,609 and 769 genomes had a variant at genomic positions 9304 and 9143, respectively.