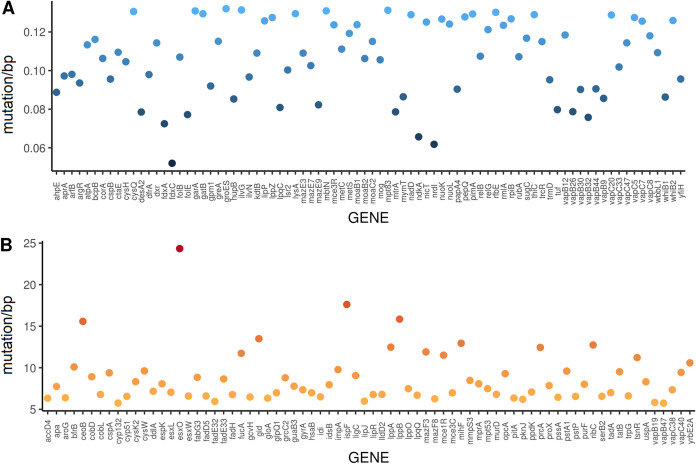
FIG 3.
Distribution of the single-nucleotide variation of the genes present in the 5th (A) and 95th (B) percentiles. (A) Fifth percentile genes. Of the genes with functional annotation to H37Rv, the gene with the lowest number of variants across the analyzed genomes in the 5th percentile was fdxC (0.05 genomes containing mutations/bp), which encodes a ferredoxin. It was noted that toxin-antitoxin genes of group II are predominant in the 5th percentile. This graph does not contain genes that were not genetically characterized with reference to H37Rv (i.e., hypothetical proteins). Information on these genes can be found in Data Set S1 in the supplemental material. Please note that in order to remove potential bias, the results were normalized by gene length (mutations/bp). (B) Ninety-fifth percentile genes. The esxO gene is the first genetically characterized gene with the highest variation (24.3 genomes containing mutations/bp) across the analyzed genomes. Genes associated with drug resistance (e.g., lppB, lppA, gidB), fadD and fadE families (e.g., fadE33, fadE32, fadH), and ESAT-6 genes are present in the 95th percentile. This graph does not contain genes that were not genetically characterized with reference to H37Rv (i.e., hypothetical proteins). Information on these genes can be found in Data Set S1 in the supplemental material. Please note that in order to remove potential bias, the results were normalized by gene length (mutations/bp).