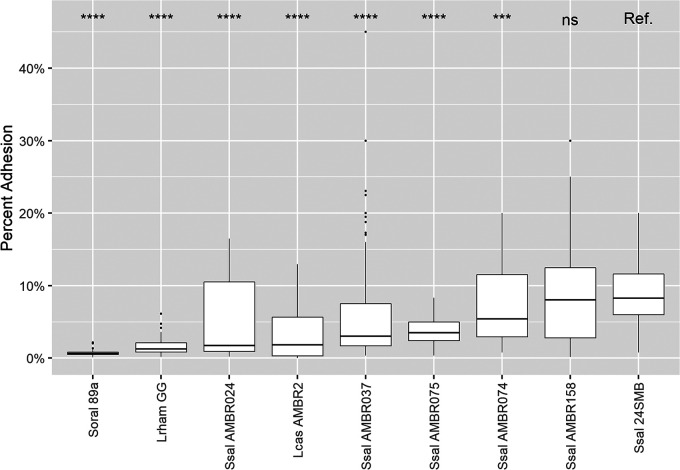
FIG 5.
Adhesion of bacterial isolates to respiratory epithelial cells (Calu-3). The adhesion of Streptococcus salivarius (Ssal) isolates obtained in the present study was statistically compared to that of S. salivarius 24SMB (38–40) of the Rinogermina probiotic nasal spray using an unpaired Wilcoxon rank sum test. S. oralis (Soral) 89a was also isolated from Rinogermina, but it showed a lower adhesion capability than all S. salivarius strains. Lacticaseibacillus casei (Lcas) AMBR2 and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus (Lrham) GG were included as examples of lactobacilli with a higher and a lower ability to adhere to respiratory epithelium, respectively (64). Isolates are sorted from lowest to highest median adhesion percentage. ns, P > 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. P values are adjusted by the Holm method.