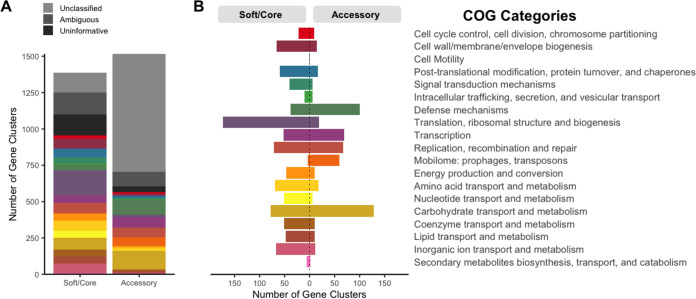
FIG 4.
The accessory genome of D. pigrum has functional enrichment for defense mechanisms, mobilome, and carbohydrate transport and metabolism genes. (A) Of the total 49,412 individual genes identified across the 28 analyzed genomes, up to 8,242 genes (16.7%) lacked a COG annotation, 5,221 (10.6%) had an ambiguous COG category annotation (more than one COG category), and 4,448 (9.0%) had an uninformative annotation (belonging to the S or R COG category). At the gene cluster (GC) level, only 37.2% of the 1,517 GCs present in the accessory genome had an informative COG assignment compared to 68.7% of the 1,388 GCs in the soft/core. (B) The number of GCs present in the accessory genome was severalfold higher than in the soft/core for the following informative COG assignments (colored categories): defense mechanisms (olive, 2.60-fold), mobilome: prophages, transposons (orange, 14.88-fold), and carbohydrate transport and metabolism (khaki, 1.66-fold). This was determined using the COG functional annotations defined in our Anvi’o analysis of the soft/core (“core” and “soft core” bins) versus accessory (“shell” and “cloud” bins). Since many GCs have individual genes with distinct COG annotations each individual gene was counted as 1/x, with x being the number of genes in each GC.