FIG 8.
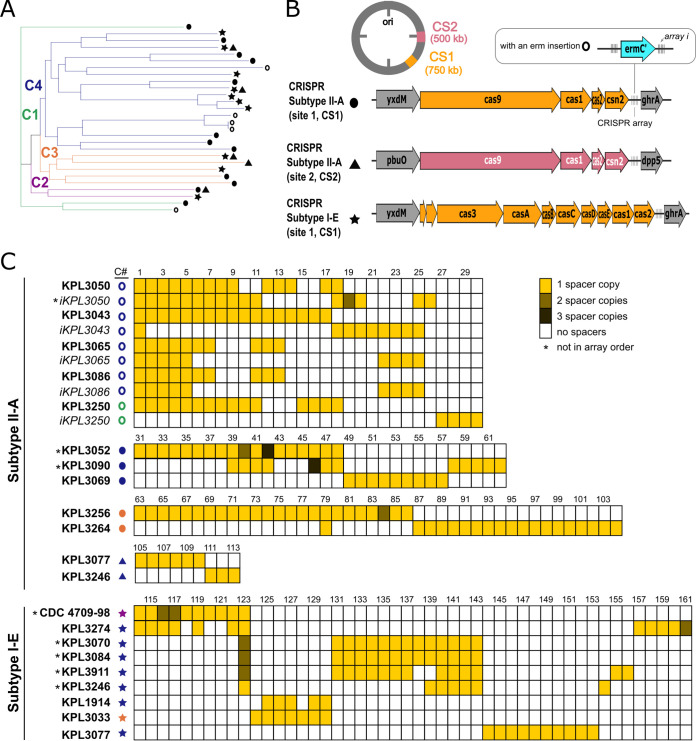
D. pigrum encodes subtype I-E and II-A CRISPR-Cas systems with a large but sparsely shared history of MGE invasion. (A) CRISPR-Cas subtype II-A (circles and triangles) and I-E systems (stars) were intermixed among strains in all four clades, with type II-A being most common (see Table S5A). Two distal clades had only a subtype II-A system (KPL3043, KPL3065/KPL3086, KPL3090, KPL3052, and KPL3069) or a subtype I-E system (KPL3070, KPL3084, and KPL391). Three genomes (KPL3077, KPL3246, and CDC2949-98) have both types of system, with each at a different locus. (B) The most common location, CRISPR-Cas system insertion site (CS1), is between the ABC transporter permease protein (yxdM) and the glyxyolytate/hydroxypyruvate reductase A (ghrA) genes. However, subtype II-A systems are also found in between the guanine/hydoxanthine permease (pbuO; NCS2 family permease) and dipeptidyl-peptidase 5 (dpp5; S9 family peptidase) genes at CRISPR-Cas insertion site 2 (CS2). Five of the strains with a subtype II-A system in CS1 had a predicted rRNA adenine N-6-methyltransferase (ermC′) gene integrated in their CRISPR arrays (open circles) (C) Representation of the spacers (see Table S5B and Text S1 in the supplemental material) found among the different CRIPSR systems in the 19 closed genomes. We found 161 unique spacers, less than one-third of which were homologous to phages and plasmids found among other Firmicutes. Strains KPL3050, KPL3250, KPL3065/KP3086, and KPL3043 shared the most spacers among the subtype II-A CRISPR-Cas system, with the distal clade of KPL3043 and KPL3065/KPL3086 sharing 15 spacers. The distal clade with KPL3070, 3084, and 3911 shared the most spacers (12) among the subtype I-E system. CRISPR-Cas systems and spacers hits were determined using the CRISPRdetect and CRISPRtarget database on 16 February 2019, while shared spacers were determined using CRIPSRCompar on 18 March 2019.