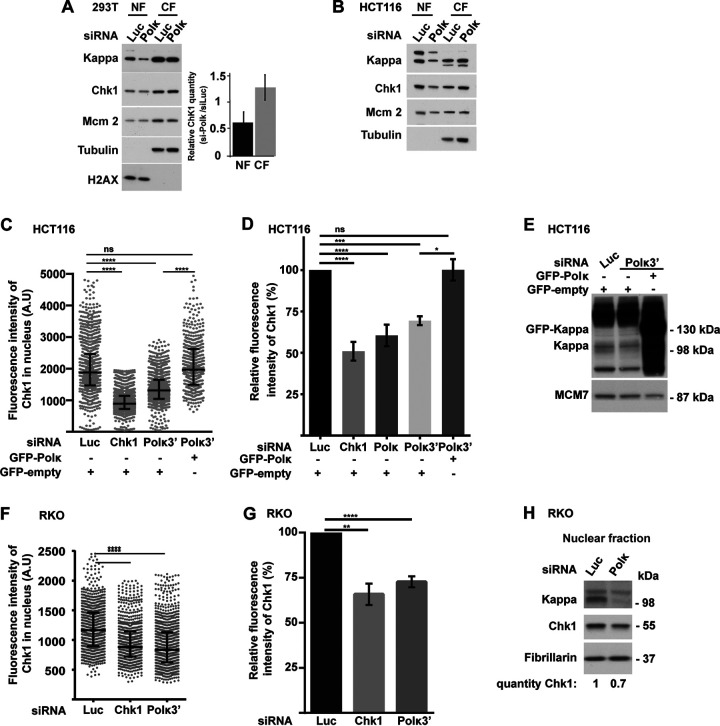
FIG 2.
Chk1 protein level is reduced in the nuclei of 293T, HCT116, and RKO cells depleted of Pol κ. (A and B) Western blot analysis of nuclear (NF) and cytoplasmic (CF) fractions from 293T (A) and HCT116 (B) cells, 48 h after transfection with a control (Luc) or Polκ siRNA. Quantifications of relative Chk1 band intensity from Western blots of 5 independent experiments with means ± SD. (C and F) HCT116 cells were transfected cotransfected with the indicated siRNAs and a vector expressing either GFP-empty or GFP-Polκ (C), and RKO cells were transfected with siRNA only (F). The fluorescence intensity of Chk1 was quantified in each nucleus. Medians with 25% and 75% interquartile ranges are represented. ***, P = 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; Mann-Whitney test. (D and G) Relative fluorescence intensity of Chk1 in nuclei of HCT116 (D) and RKO (G) cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs (G) or both with a vector expressing either GFP-Polκ or GFP-empty (D). Values are the means (±SEM) of medians of three or four independent experiments. Relative fluorescence intensity was adjusted to the siLuc condition. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; t test. (E) Western blot analysis of Pol κ and GFP-Polκ in nuclear extracts of HCT116 48 h after cotransfection with a control siRNA (Luc) or targeting the 3′ UTR of Pol κ (Polκ3′) with a vector expressing either GFP-empty or GFP-Polκ. MCM7 is shown as a loading control. (H) Western blot analysis of Chk1 and Pol κ in RKO nuclear extracts 48 h after transfection with a control siRNA (Luc) or Polκ siRNA. Fibrillarin is shown as a protein-loading control. Quantification of Chk1 is relative to the siLuc condition.