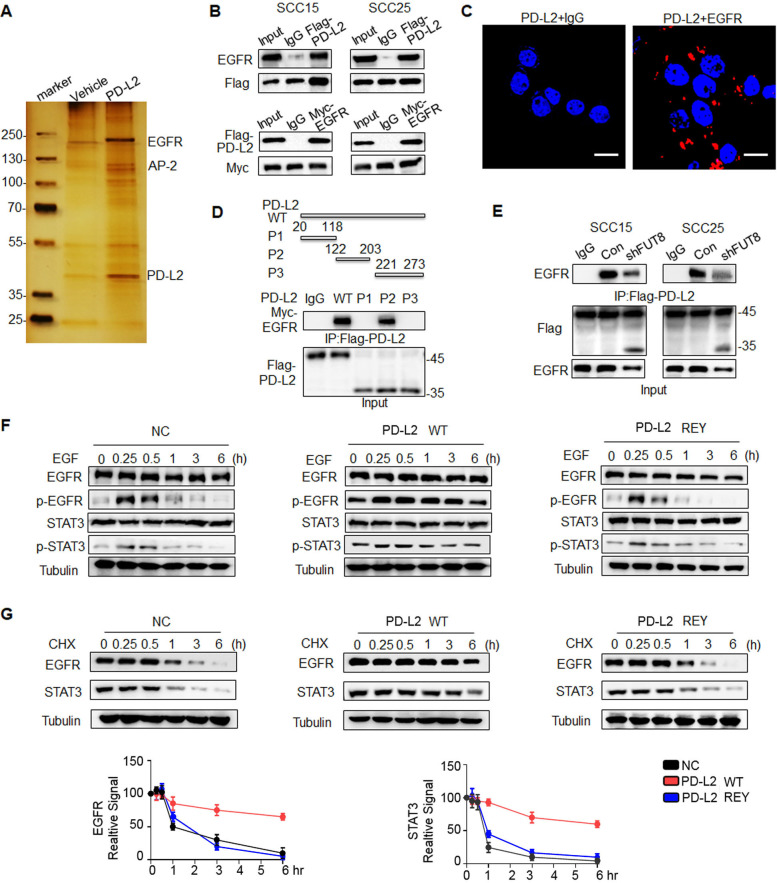
Figure 5.
Glycosylated PD-L2 interacts with EGFR and upregulates EGFR/STAT3 signaling activity. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) followed by mass spectrometry were performed to identify the proteins that bind to PD-L2. (B) Co-IP analysis of the interaction of EGFR with PD-L2 in SCC15 and SCC25 cells. (C) In situ proximity ligation assay results revealed the direct interaction of PD-L2 with EGFR in SCC15 cells. Scale bar, 20 µm. (D) Identification of the PD-L2 essential domains required for interactions with EGFR. P1, Ig-like V-type domain; P2, Ig-like C2-type domain; P3, transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic domain. (E) Silencing FUT8 abrogated EGFR/PD-L2 interaction. (F) Negative control-expressing, PD-L2 WT-expressing, or REY mutant-expressing SCC15 cells were serum-starved for 4 hours and treated with EGF (20 ng/mL). Protein expression was analyzed using the indicated antibody. (G) Cells were treated with CHX (20 µM) for the indicated times and analyzed using immunoblotting with anti-EGFR and anti-STAT3 antibodies (top panel). The intensity of each band was quantified using ImageJ software (bottom panel). EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FUT8, fucosyltransferase; PD-L2, programmed death ligand 2; REY, PD-L2 REY mutant, in which the amino acid of R168, E171 and Y174 were substituted by Alanine; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; WT, wild type.