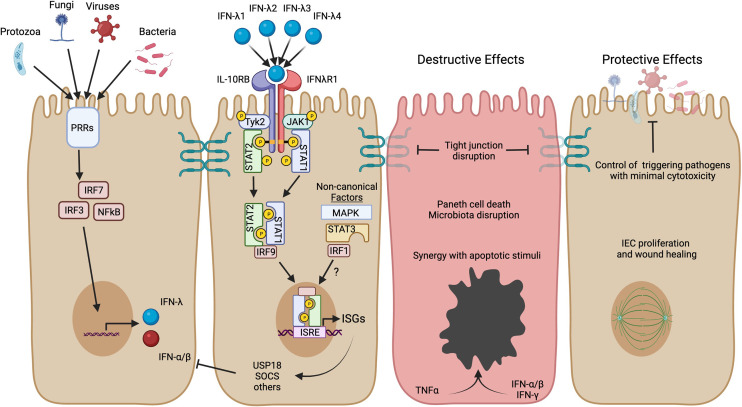
Figure 1.
IFN-λ induction, signaling, and potential roles in IBD. Production of IFN-λ can be stimulated by microbial activation of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and stimulation of downstream transcription factors (IRF3, IRF7, NFκB). These same transcription factors can also stimulate IFN-α/β, but IECs are able to preferentially produce IFN-λ (19). The four subtypes of human IFN-λ bind to the heterodimeric IFN-λ receptor to activate JAK/STAT signaling and transcription of ISGs. IFN-λ activates the canonical heterotrimeric transcription factor ISGF3 (STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9) to upregulate a core set of ISGs, including direct-acting antiviral effectors and mediators of negative feedback such as USP18 and SOCS genes. Other non-canonical factors such as MAPK, STAT3, and IRF1 can further influence the magnitude and scope of ISGs expressed and may have distinct roles in the context of inflammatory disease. The figure highlights possible detrimental and protective roles for IFN-λ in the context of IBD based on human organoid studies and mouse models of intestinal inflammation (see text for more detail). Created in BioRender.com.