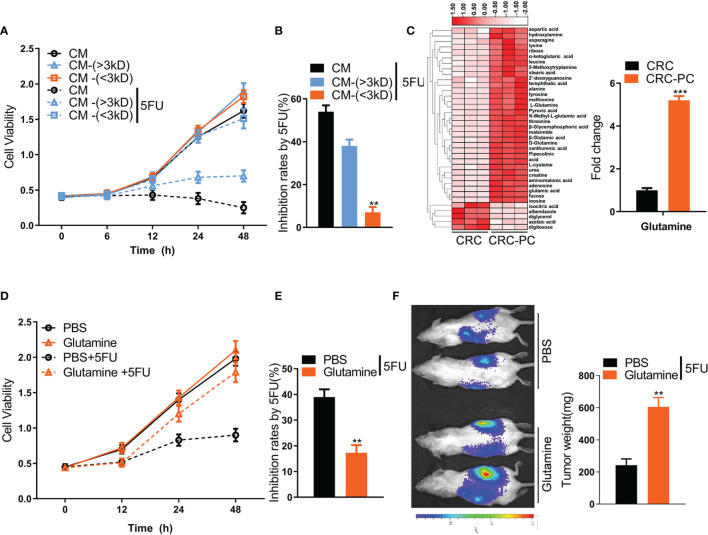
Figure 2.
Adipocyte-derived glutamine (Gln) promotes resistance to 5FU chemotherapy in mouse CRC cells. (A) CM was separated into two fractions based on size: CM-(<3 KD) and CM-(>3 KD). The cell viability of CT26 cells treated with CM, CM-(<3 KD) or CM-(>3 KD) plus with/without 5FU (10 μmol/L) was measured. (B) The growth inhibition rates by 5FU were calculated according to (A) (n = 5, **P < 0.01). (C) Left, heatmap showing differential metabolic profiles of fat tissues from the peritoneum of the in situ CRC mode (CRC) (n = 3) and the peritoneal metastasis model (CRC-PC) (n = 3). The color represents the metabolite concentration of each sample calculated by peak area normalization method. Right, fold change of Gln level between the CRC-PC and the CRC group (n = 3, ***P < 0.001). (D) Cell viability of CT26 cells treated with 5FU (10 μmol/L), Gln (2 mM) or Gln (2 mM) plus 5FU (10 μmol/L). (E) Inhibition rates by 5FU according to the data in (D) (n = 5, **P < 0.01). (F) Gln-induced chemoresistance to 5FU. Left, tumor growth in peritoneal xenografts. Right, tumor weight. The tumors were isolated and weighed on day 17 (n = 5, **P < 0.01).