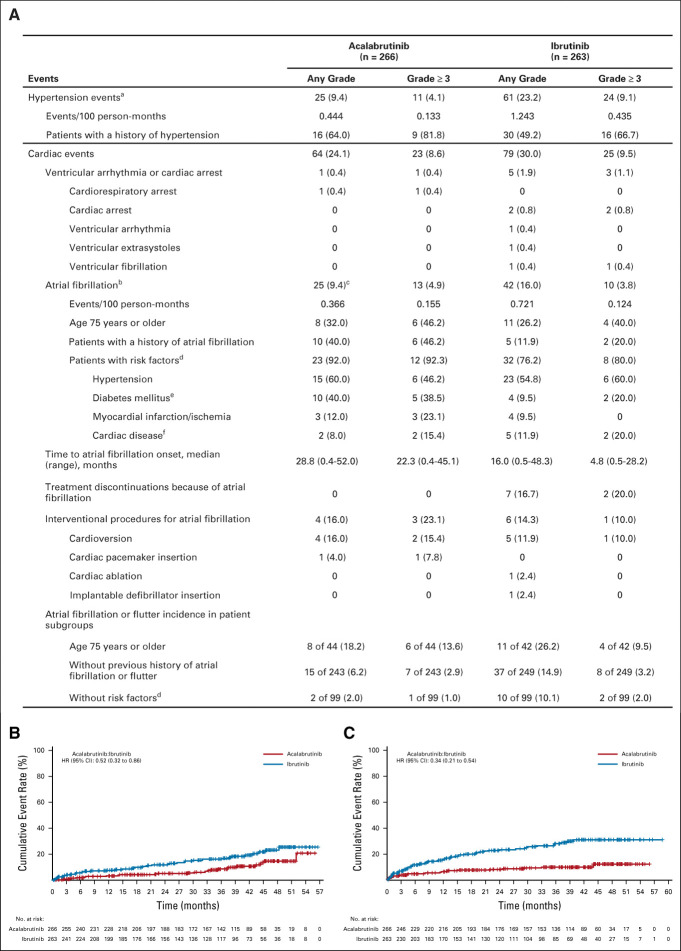
FIG 4.
(A) Summary of hypertension and selected cardiac events and cumulative incidence of (B) atrial fibrillation and (C) hypertension. NOTE. Data are reported as no. (%) unless otherwise specified; within each event type (hypertension, cardiac events, and atrial fibrillation), percentages are based on the number of patients with the event. aIncludes events with the preferred terms of hypertension, blood pressure increased, and blood pressure systolic increased; two-sided P value on the basis of Barnard’s exact test without multiplicity adjustment, P < .001 (any-grade) and P = .0214 (grade 3 or higher). bIncludes events with the preferred terms of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter (a patient was only counted once if he or she experienced both types of events); atrial flutter was reported in one patient in the acalabrutinib arm and two patients in the ibrutinib arm (one of the two ibrutinib patients also had an atrial fibrillation event and was counted only once for the combined atrial fibrillation or flutter term). cPart of the multiple testing procedure; difference in any-grade incidence rates was −6.6% (95% CI: −12.2 to −0.9), P = .02. dRisk factors for atrial fibrillation were based on medical review. eIncludes patients with a history of diabetes mellitus or type 2 diabetes mellitus. fIncludes patients with a history of coronary artery bypass, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, cardiac failure chronic, or cardiac failure congestive. HR, hazard ratio.