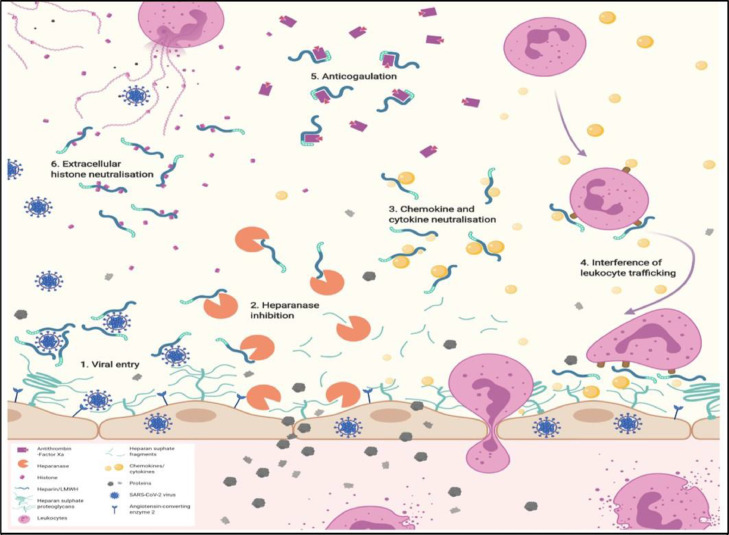
Fig. 4.
Summary of the potential beneficial mechanisms of heparin/low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) underlying treatment of COVID-19 patients. 1. Reducing viral entry. Heparan sulfate, and heparin/LMWH have been shown to interact with SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. 2. Inhibition of heparanase activity. Heparin/LMWH has been shown to inhibit heparanase activity, which is increased in COVID-19 and associated with disease severity. 3. Neutralization of the biological effect of chemokines, and cytokines. Heparin/LMWH interact with chemokines, and cytokines, including those produced in the ‘cytokine storm’ in COVID-19. 4. Interference with leukocyte trafficking. Heparin/LMWH neutralization of chemokine, and cytokines may impact on leukocyte recruitment and trafficking to sites of inflammation, either via neutralization of chemokine, and cytokines or through direct interaction with leukocyte cell surface ligands, i.e. selectins, and integrins, to prevent leukocyte attachment, and extravasation. 5. Anticoagulation. Heparin/LMWH promotes anticoagulation via anti-thrombin III binding. 6. Neutralization of extracellular cytotoxic histones. Heparin/LMWH act as a neutralizing compound for histones via ionic interactions of the negatively charged chemical groups with the positively charged extracellular histones released during COVID-19. (B. Buijsers et al. / EBioMedicine 59 (2020) 102969, Permission obtained from original author for distribution provided original work cited.)