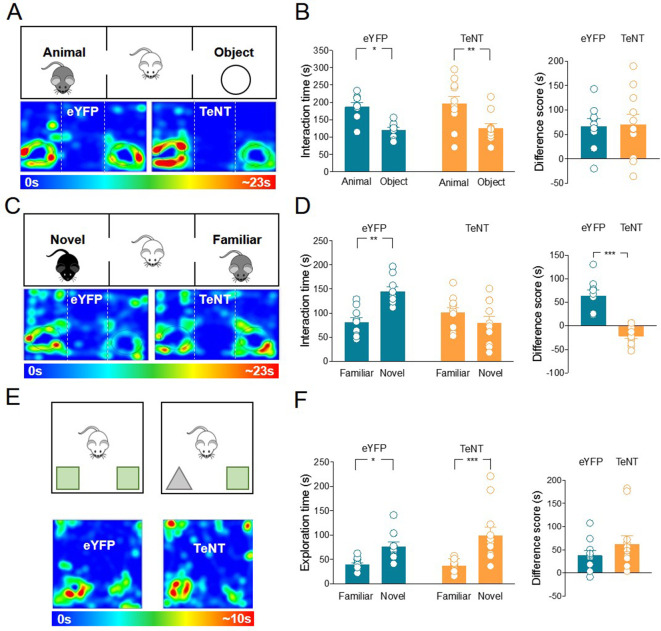
Figure 3. Inhibition of acetylcholine (ACh) release from medial septum/diagonal band of Broca (MSDB) ChAT+ neurons impairs social novelty but not object recognition.
(A) Top: schematic illustration of the sociability task in the three-chamber test. Bottom: representative heat map showing the time spent by an eYFP (left) or a TeNT (right) mouse in exploring the animal (left) and the object (right). (B) Left: aligned dot plot showing interaction time spent to explore the animal and the object during sociability task in eYFP (control, green, n = 9) and TeNT mice (orange, n = 11) (eYFP: 187 ± 12 vs 121 ± 7.7 s, p = 0.018; TeNT: 197 ± 20 vs 127 ± 12 s, p = 0.005; one-way ANOVA). Right: aligned dot plot showing the sociability score in eYFP (control, green, n = 9) and TeNT mice (orange, n = 11) (eYFP: 66.8 ± 15 s; TeNT: 70.5 ± 21 s, p = 0.94; Mann–Whitney test). (C) Top: schematic illustration of the social novelty task in the three-chamber test. Bottom: representative heat map showing the time spent by an eYFP (left) or a TeNT (right) mouse in exploring the novel animal (left) and the familiar one (right). (D) Left: aligned dot plot showing interaction time spent to explore the novel and the familiar animal in the social novelty task in eYFP (control, green, n = 9) and TeNT (orange, n = 11) mice (eYFP: 145 ± 10 vs 81.2 ± 10 s, p = 0.002; TeNT: 79.8 ± 13 vs 101 ± 10 s, p = 0.47; one-way ANOVA). Right: aligned dot plot showing the social novelty score in eYFP (control, green, n = 9) and TeNT (orange, n = 11) mice (eYFP: 64.1 ± 12 s; TeNT: −21.7 ± 5.8 s, p < 0.0001; Mann–Whitney test). (E) Top: schematic illustration of the novel object recognition (NOR) test. Bottom: representative heat map showing the time spent by an eYFP (left) or a TeNT (right) mouse in exploring the novel (left) and the familiar (right) object. (F) Left: aligned dot plot showing the exploration time spent to explore the familiar and the novel object during NOR task in eYFP (control, green, n = 11) and TeNT (orange, n = 12) mice (eYFP: 76.6 ± 8.8 vs 39 ± 3.6 s, p = 0.03; TeNT: 99.9 ± 16 vs 37.6 ± 9.8 s, p = 0.0002; one-way ANOVA). Right: aligned dot plot showing the exploration score in eYFP (control, green, n = 11) and TeNT (orange, n = 12) mice (eYFP: 37.6 ± 9.8 s; TeNT: 62.7 ± 17 s, p = 0.38; Mann–Whitney test). Open circles are values from single animals and bars are mean ± SEM. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001.