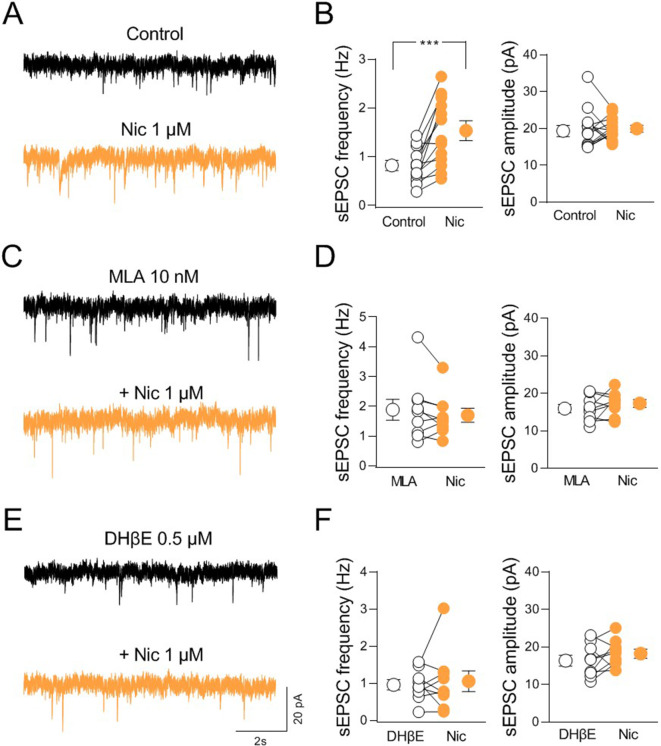
Figure 7. nAChR-mediated modulation of synaptic transmission in CA2.
(A) Sample traces showing spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) of a CA2 pyramidal neuron recorded at ECl− in control (black) and in the presence of nicotine (1 μM; orange). (B) Aligned dot plots showing the mean frequency (left) and amplitude (right) of sEPSCs recorded from CA2 pyramidal neurons in control (black) and in the presence of nicotine (1 μM; orange) (n = 13 cells; frequency: control: 0.81 ± 0.1 Hz, Nic: 1.5 ± 0.2 Hz; p = 0.0005; amplitude: control: 19.9 ± 1.4 pA, Nic: 19.7 ± 0.8 pA; p = 0.76; Wilcoxon test). (C) Sample traces showing sEPSCs of a CA2 pyramidal neuron recorded at ECl− in the presence of α7 nAChR antagonist methyllycaconitine (MLA, (10 nM; black)) and in the presence of MLA plus nicotine (1 μM; orange). (D) Aligned dot plots showing the mean frequency (left) and amplitude (right) of sEPSCs recorded from CA2 pyramidal neurons in the presence of MLA (10 nM; black) and in the presence of MLA plus nicotine (1 μM; orange) (n = 9 cells; frequency: MLA: 1.9 ± 0.3 Hz, MLA+ Nic: 1.7 ± 0.2 Hz; p = 0.34; amplitude: MLA: 15.9 ± 1.1 pA, MLA+ Nic: 17.3 ± 1.0 pA; p = 0.36; Wilcoxon test). (E) Sample traces showing sEPSCs of a CA2 pyramidal neuron recorded at ECl− in the presence of non-α7 nAChR antagonist dihydro-β-erythroidine (DHβE, 0.5 μM; black) and in the presence of DHβE plus nicotine (1 μM; orange). (F) Aligned dot plots showing the mean frequency (left) and amplitude (right) of sEPSCs recorded from CA2 pyramidal neurons in the presence of DHβE (0.5 μM; black) or DHβE plus nicotine (1 μM; orange) (n = 9 cells; frequency: DHβE: 0.9 ± 0.1 Hz, DHβE + Nic: 1.05 ± 0.3 Hz; p > 0.99; amplitude: DHβE: 16.3 ± 1.5 pA, DHβE + Nic: 18.2 ± 1.2 pA; p = 0.25; Wilcoxon test). Open or closed circles represent values from single cells. Laterally located circles represent mean ± SEM. ***: p < 0.001.