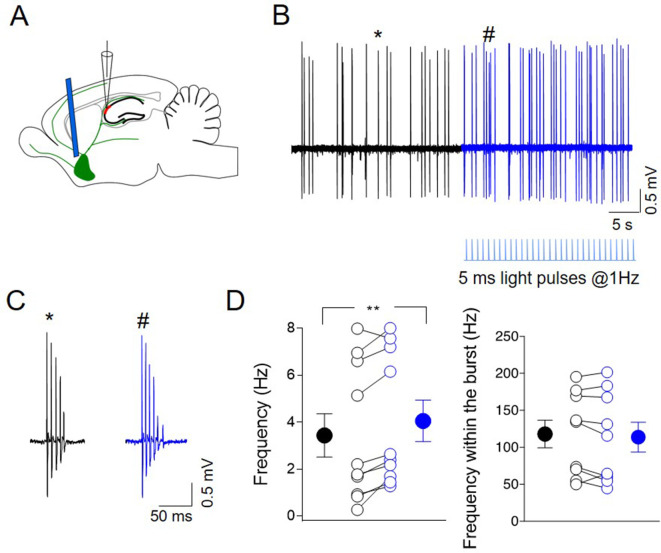
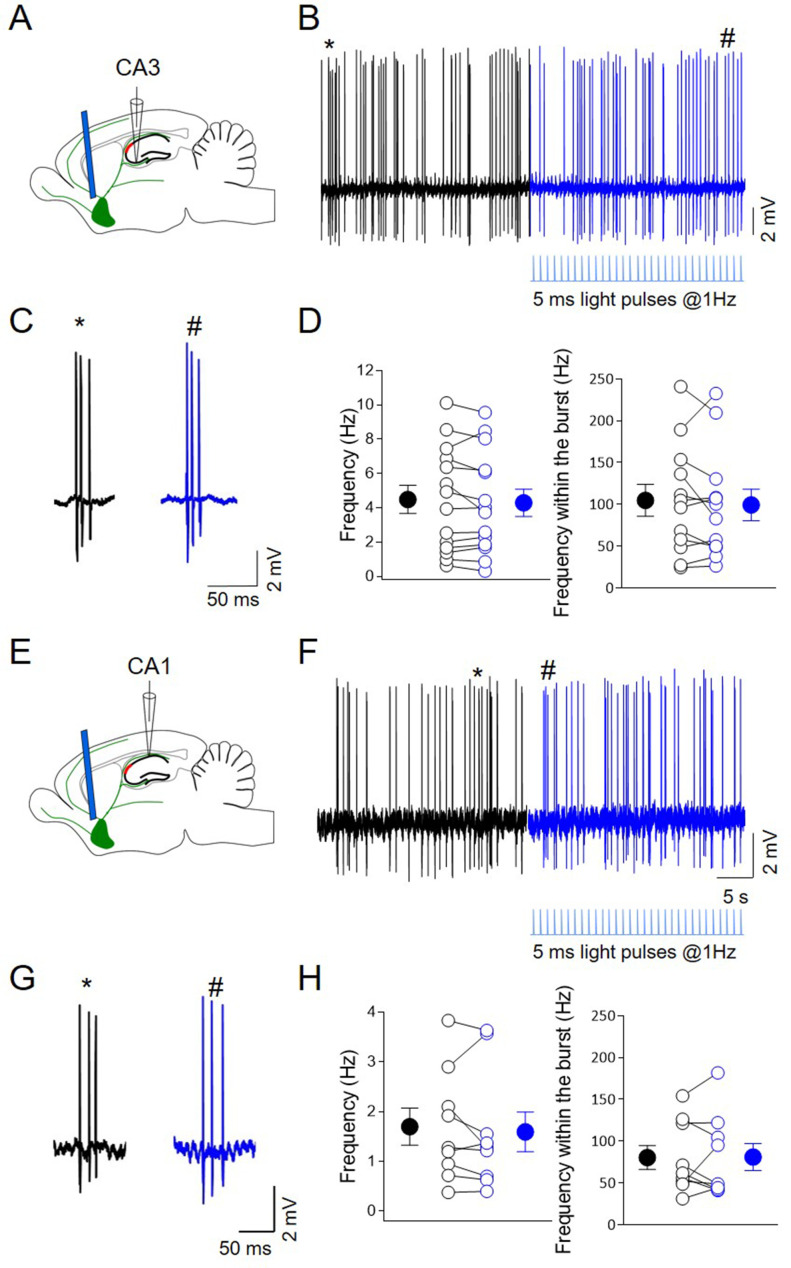
Figure 9. Photoactivation of ChAT+ neurons in medial septum/diagonal band of Broca (MSDB) controls CA2 output.
(A) Schematic illustration showing the experimental settings of in vivo juxtacellular recordings combined with light stimulation of MSDB ChAT+ neurons expressing channelrhodopsin (ChR2). (B) Representative trace showing spontaneous firing from a CA2 bursting neuron in control (black) and during ChR2 activation (blue) via light pulses (below the trace). (C) Individual bursts in (B) (asterisk and hashtag for control and light activation, respectively) shown on an expanded time scale. (D) Left: aligned dot plot showing the frequency of spikes in control (black) and during light activation of ChAT+ neurons in the MSDB (blue) (n = 9 cells; control: 3.62 ± 1.0 Hz; light: 4.26 ± 0.97 Hz; p = 0.012, Wilcoxon test); right: aligned dot plot showing the frequency of spikes within the bursts in control and during light activation of ChAT+ neurons in the MSDB (n = 9 cells; control: 118 ± 19 Hz; light: 114 ± 20 Hz; p = 0.36, Wilcoxon test). Open circles represent values from single cells. Closed circles represent mean ± SEM. **: p = 0.01.