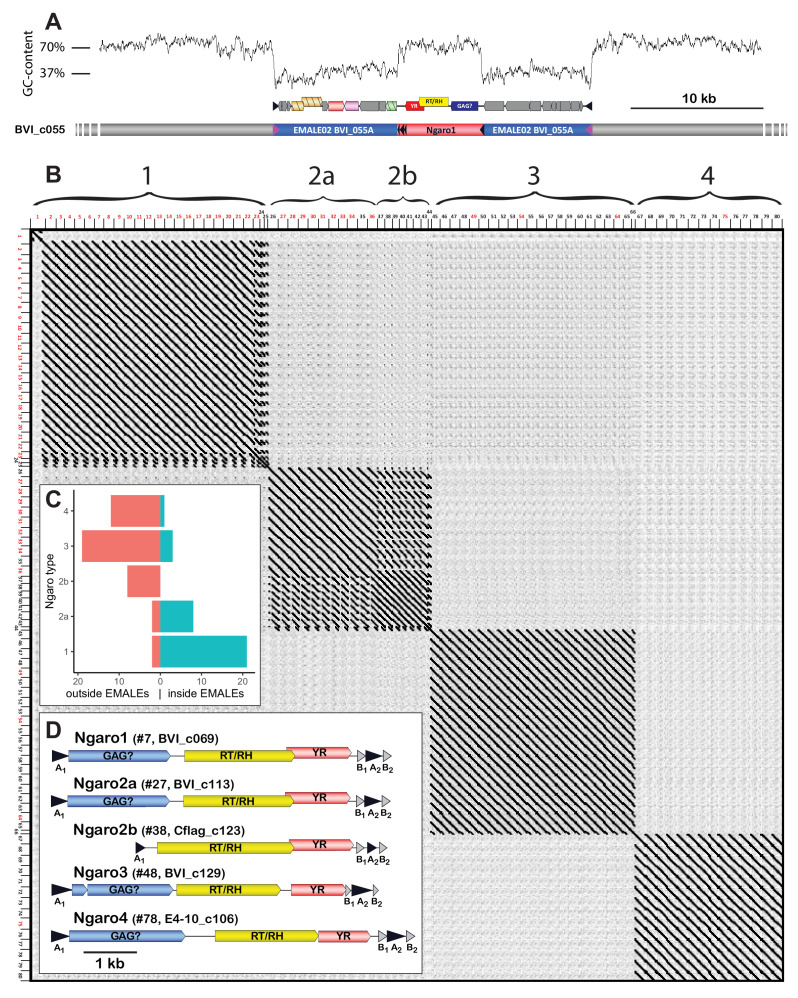
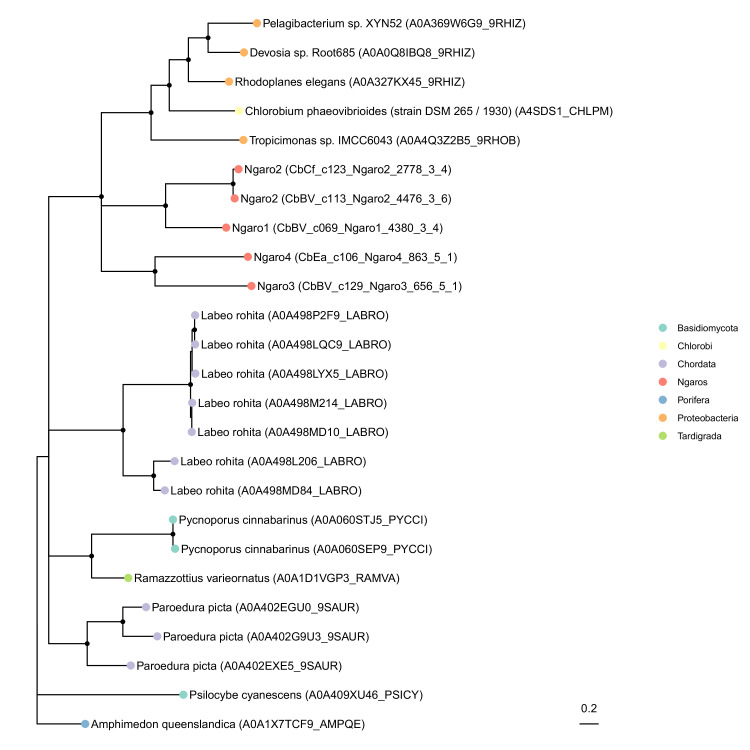
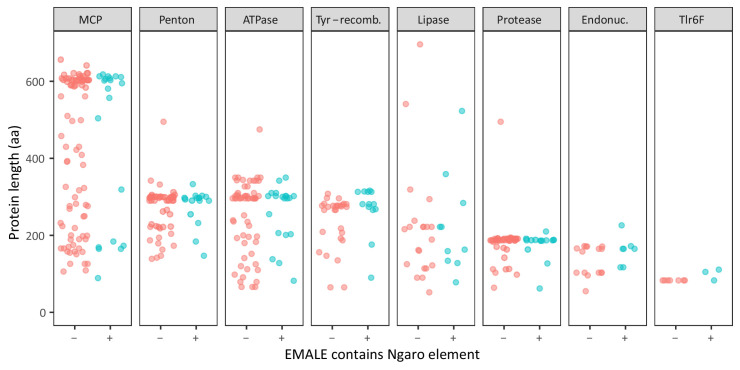
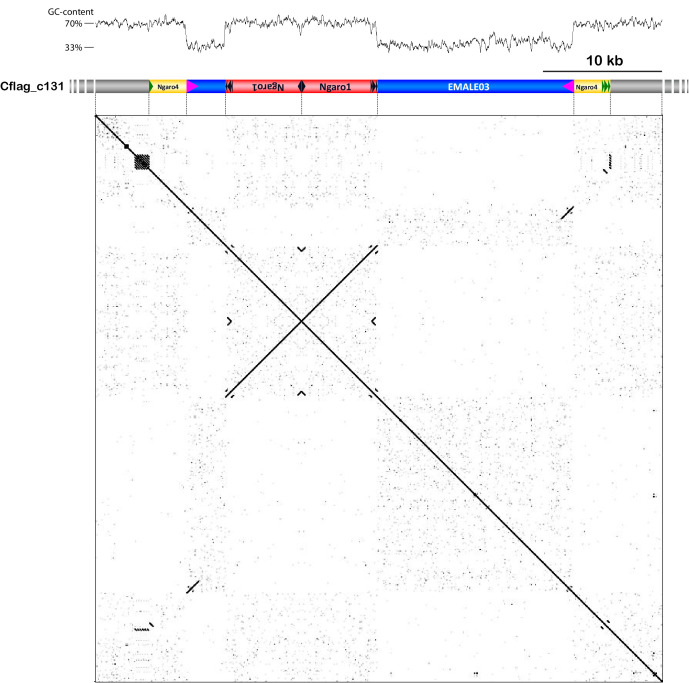
Figure 5. Ngaro retrotransposons in Cafeteria burkhardae.
(A) Genomic profile of an EMALE-integrated Ngaro element showing a GC-content graph (top), open reading frame (ORF) organization of EMALE and Ngaro (middle), and a schematic overview of the three genomic entities (bottom; host: gray, EMALE: blue, Ngaro: red). (B) Self-versus-self DNA dot plot of 80 concatenated Ngaro sequences. Block patterns define Ngaro types 1–4. Ngaros are numbered according to Supplementary file 1, with red numbers indicating retrotransposons inserted in EMALEs. (C) Distribution of Ngaro integration loci in EMALE and host DNA. Ngaro types 1 and 2a show a clear preference for EMALE loci, in contrast to Ngaro types 2b, 3, and 4 that are mostly found in host loci. (D) Coding potential of C. burkhardae Ngaro retrotransposons, shown for one example per type with their host strain and contig numbers listed. Triangles indicate direct repeats. GAG, group specific antigen; RT, reverse transcriptase; RH, ribonuclease H; YR, tyrosine recombinase.