Figure 8.
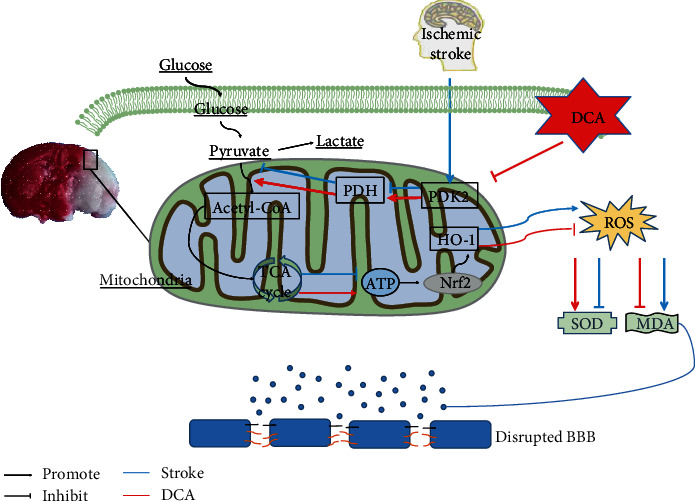
Sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) improves glycolysis by inhibiting PDK2 and activating PDH and promotes the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, which then enters the TCA cycle so as to produce ATP, thus improving glycolysis. Meanwhile, it activates the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway to increase the activity of SOD, inhibit the generation of MDA, and reduce oxidative stress, thereby alleviating the damage of the blood-brain barrier and facilitating the recovery of oxidative metabolism.
