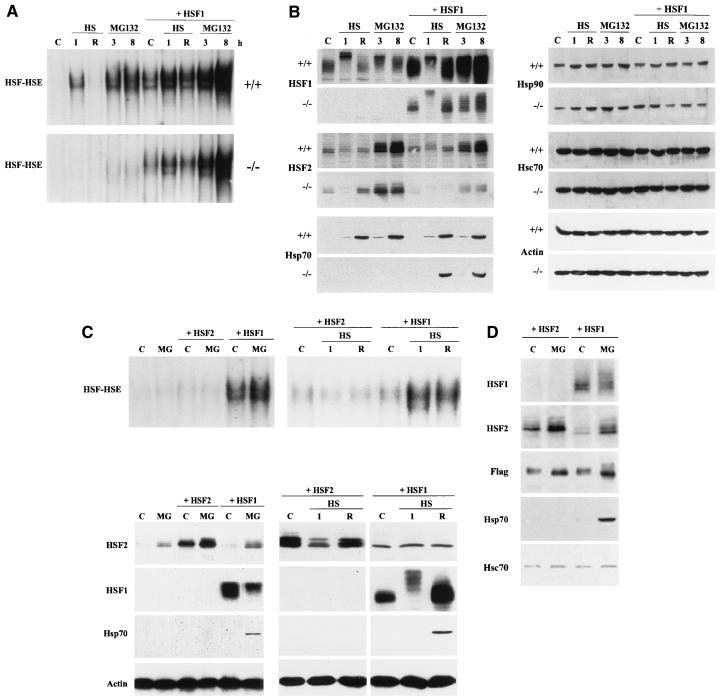
FIG. 3.
HSF1, but not HSF2, can restore Hsp70 expression. (A) Whole cell extracts from control (C), heat-shocked (HS; 42°C for 1 h without [1] or with [R] a 3-h recovery at 37°C), and MG132-treated (10 μM for 3 and 8 h) wild-type (+/+) and hsf1−/− MEF cells, as well as wild-type and hsf1−/− cells transiently transfected with mouse HSF1 (+ HSF1), were analyzed as described for Fig. 1A. (B) The samples described above were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against HSF1, HSF2, Hsp70, Hsp90, Hsc70, and actin. (C) Whole cell extracts from control (C), heat-shocked (HS; 42°C for 1 h without [1] or with [R] a 3-h recovery at 37°C), and MG132-treated (10 μM for 8 h) MEF cells deficient for HSF1, as well as hsf1−/− cells transiently transfected with mouse HSF2 (+ HSF2) or HSF1 (+ HSF1), were subjected to gel mobility shift analysis (upper panels) and Western immunoblotting (lower panels) using antibodies against HSF2, HSF1, Hsp70, and actin. (D) Whole cell extracts from control (C) and MG132-treated (10 μM for 8 h) hsf1−/− cells transiently transfected with Flag epitope-tagged mouse HSF1 (+ HSF1) and HSF2 (+ HSF2) were subjected to Western immunoblotting using antibodies against HSF1, HSF2, Flag, Hsp70, and Hsc70.