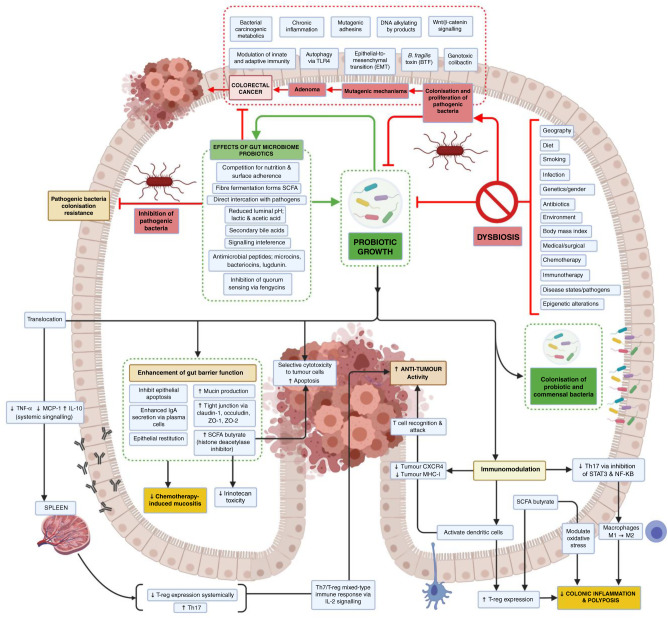
Fig. 2. Summary of the putative mechanisms of therapeutic microbiota on gut microbiome homeostasis and colorectal cancer carcinogenesis by immune-mediated and non-immune-mediated mechanisms.
Therapeutic microbiota may potential CRC prevention through (1) enhancement of gut barrier function, (2) immunomodulation (activation of DCs, macrophages, tumour CXCR4 and MHC-1, systemic Th7/T-reg immune response) and modulation of oxidative stress to reduce colonic inflammation and increase immune-mediated anti-tumour activity, (3) promotion of an advantageous gut microenvironment that inhibits pathogenic bacterial colonisation, (4) selective cytotoxicity to tumour cells. SCFA short-chain fatty acids, CXCR4 CXC cytokine receptor 4, MHC-1 major histocompatibility complex class I, Th17 T helper cell 17, T-reg, T-regulatory cell, NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa light-chain enhancer of activated B cells, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Created with BioRender.com.