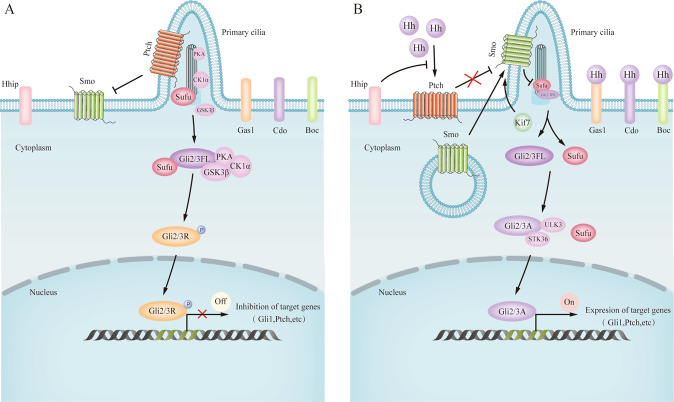
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of paracrine Hh signalling in the mammalian intestine.
Hh ligands are secreted by intestinal epithelial cells. The signals are received by various types of mesenchymal cells. In the absence of Hh ligands (A), the receptor Ptch localises in the primary cilium (PC) and inhibits Smo, a necessary receptor to deliver Hh signals, movement to the primary PC. Under such cases, Sufu restrains the full-length form of Glioma-associated oncogenes 2/3 (Gli2/3FL) in the cytosol, where they are partially phosphorylated and proteolyzed by a multiple protein kinase complex composed of PKA, GSK3β, and CK1α. This generates the repressor form, namely Gli2/3 repressor (Gli2/3 R), which translocates to the nucleus to bind to and inhibit the expression of Hh target genes. In the presence of Hh ligands (B), binding of Hh ligands to Ptch removes the inhibitory action of Ptch on Smo and drives the accumulation and activation of Smo in the PC, leading to subsequent inhibition of Sufu by Smo and the dissociation of Gli2/3FL. kinesin family member 7 (Kif7), a core regulator of mammalian Gli proteins, moves from the basal body to the tip of the PC in a Hh-dependent manner, assisting Smo accumulation in the PC. Gil2/3FL is then phosphorylated by serine/threonine protein kinases, including ULK3 and STK36, resulting in the formation of Gli2/3 activator (Gle2/3 A) and translocation into the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, Gli2/3 A upregulates the transcriptional targets of Hh signalling, including Ptch and another Hh-binding protein, Hhip. Gas1, Cdo, and Boc are co-receptors that promote Hh-Ptch binding. Arrows and blunt ends lines indicate activation and inhibition, respectively. Ptch Patched, Smo Smoothened, Hhip Hedgehog interacting protein, Gas1 Growth arrest-specific gene 1, Cdo Cell adhesion molecule-related, downregulated by oncogenes; Boc, Brother of Cdo; Gli2/3FL, full-length form of Glioma-associated oncogenes 2/3, Gli2/3 A activator form of Glioma-associated oncogenes, Gli2/3 R repressor form of Glioma-associated oncogenes 2/3, Sufu Suppressor of Fused, Kif7 kinesin family member 7, PKA protein kinase A, GSK3β glycogen synthase kinase 3β, CK1α casein kinase 1α STK36 serine/threonine protein kinase 36, ULK3 UNC-51-like kinase 3.