Fig. 2. Crosstalk between Hedgehog and other pathways in the intestinal tract.
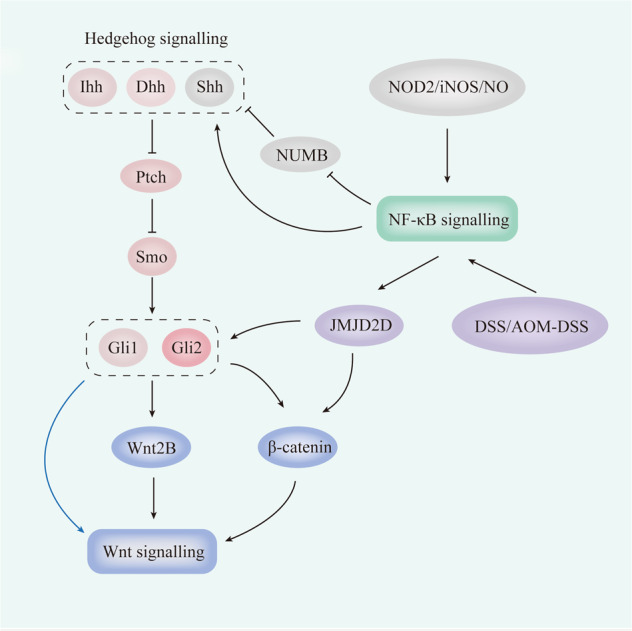
β-catenin is a target gene of Hh/Gli2 signalling. Hh signalling can enhance Wnt signalling by inducing the expression of β-catenin in the colon during IBD and CAC. Epithelial Ihh and Shh upregulate the expression of Wnt2B in intestinal mesenchymal cells during chronic intestinal inflammation. The subepithelial Gli1-positive mesenchymal cells express high levels of Wnt2B. Dhh-activated Hh signalling positively regulates epithelial cell-produced Wnt2B expression following IEC injury and regeneration. Gli1-expressing mesenchymal cells serve as a reserve Wnt source during recovery from DSS-induced colitis in mice, thereby enhancing Wnt signalling. Shh is a target gene of NK-κB and can be induced by the activation of NK-κB in inflamed intestinal epithelial cells. NK-κB mediates NOD2-iNOS/NO-NUMB-mediated Shh signalling activation, which plays a role in modulating inflammatory responses in IBD. TNF-a/NF-κB signalling promotes the activation of Hh/Gli1/Gli2 signalling in DSS- or AOM/DSS-induced colitis. Arrows and blunt ends indicate activation and inhibition, respectively. The blue arrows indicate a special condition where Gli1 is overexpressed in mesenchymal cells. NOD2 the nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2, iNOS inducible nitric-oxide synthase, NO nitric oxide, NF-κB nuclear factor-kappaB, Ihh Indian hedgehog, Dhh Desert hedgehog, Shh Sonic hedgehog, Ptch Patched, Smo Smoothened, Gli1 Glioma-associated oncogene 1, Gli2 Glioma-associated oncogene 2, AOM-DSS azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulphate, JMJD2D jumonji domain-containing protein 2D.
