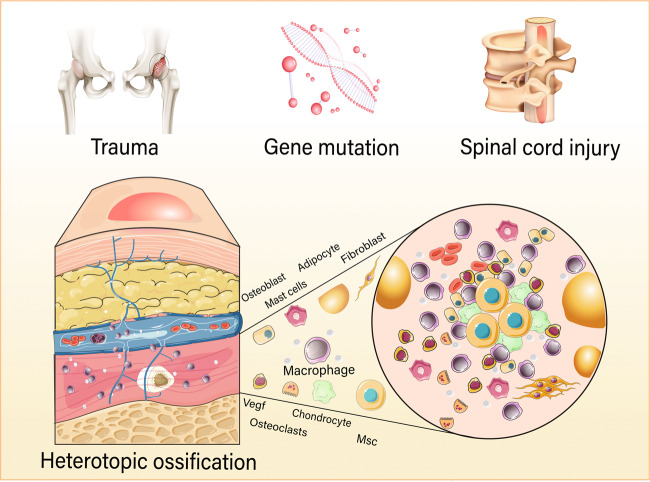
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of heterotopic ossification (HO) formation.
HO is the formation of extraskeletal bone in soft tissues, which is caused by neurogenic trauma (spinal cord injury, encephalitis, etc.), gene mutation, and severe skeletal muscle trauma. HO is characterized as a multifactorial pathology and inflammatory disease. Inflammation is a common feature of acquired and genetic HO, which manifests as pain, warmth, redness, and swelling. Macrophages, mast cells, MSCs, chondrocytes, bone cells, fibroblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoblasts exist in lesion areas of vessels and muscles. Macrophages in the inflammatory environment influence osteogenic differentiation of MSCs and angiogenesis, the key steps of HO development.