Figure 6.
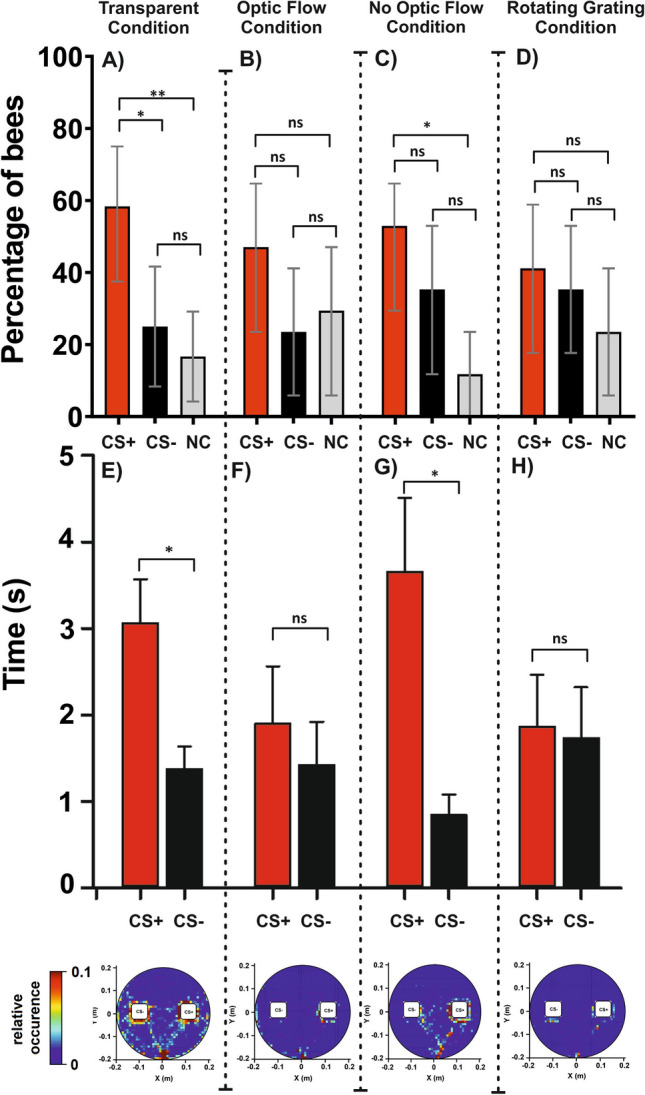
Test performances (1st choice and fixation time) in a color discrimination learning task under four different background conditions. Panels (A–D) refer to the 1st choice and show the percentage of bees responding to the CS+ (red), to the CS− (black) or not making any choice (NC; gray) during a retention test performed in extinction conditions after a 10-trial training. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ns: non-significant. (A) In the ‘Transparent Condition’ (N = 24), the blue and green cuboids were displayed against a dark background. (B) In the ‘Vertical Grating—Optic Flow Condition’ (N = 17), the cuboids were presented against a red-and-black vertical grating, which was coupled to the bee’s movements (closed-loop conditions). (C) In the ‘Vertical Grating—No Optic Flow Condition’ (N = 17), the cuboids were displayed against the same red-and-black grating but motion cues from the background were suppressed by keeping it constantly fixed to the bee’s gaze. (D) In the ‘Rotating Vertical Grating Condition’ (N = 17), the cuboids were shown against the same red-and-black grating, which was rotated counterclockwise around the virtual arena at a constant speed, thus generating a constant optic flow even when the bee did not move. Panels (E–H) refer to the fixation time, i.e. the time spent fixating either the CS+ or the CS− during the test. Bars represent the mean fixation time. Error bars indicate the standard error f the mean. *: p < 0.05; ns: non-significant. (E) ‘Transparent Condition’ (N = 24). (F) ‘Vertical Grating—Optic Flow Condition’ (N = 17). G) ‘Vertical Grating—No Optic Flow Condition’ (N = 17). (H) ‘Rotating Vertical Grating Condition’ (N = 17). The bottom row shows the heat map corresponding to each condition. Each heat map shows the cumulative coordinates occupied by the bees under each background condition during the test. Coordinates were binned into 1 cm2. Warmer colors depict locations more frequently occupied (see color bar). The highest frequency is cut down to 10% of the maximum on the color bar. The rewarded stimulus was placed arbitrarily on the right.
