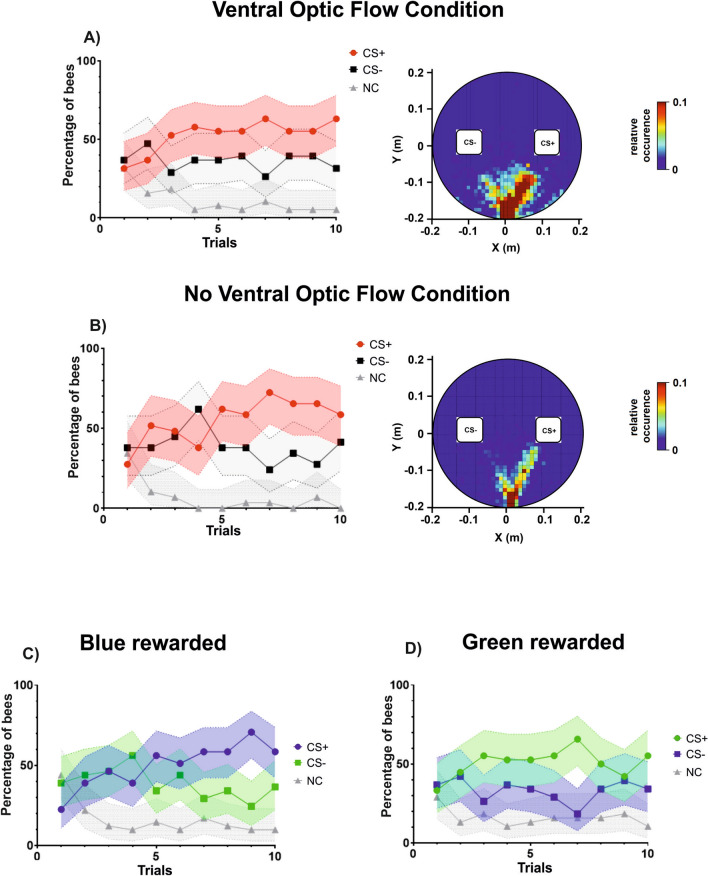
Figure 7.
Acquisition performances in a color discrimination learning task under two different ventral optic-flow conditions. (A) Color discrimination learning with motion cues available ventrally on the treadmill (N = 38). Left: Acquisition curves in terms of the percentage of bees responding to the CS+ (red), to the CS− (black) or not making any choice (NC; gray) during the ten conditioning trials. The pink, light gray and gray areas around the curves represent the 95% confidence interval of CS+, CS− choices and NC, respectively. Right: Heat map showing the cumulative coordinates occupied by the bees trained under this condition during the ten training trials. Coordinates were binned into 1 cm2. Warmer colors depict locations more frequently occupied (see color bar). The highest frequency is cut down to 10% of the maximum on the color bar. While the side of the rewarded stimulus was randomized along conditioning trials, it was placed arbitrarily on the right in the heat maps. (B) Color discrimination learning in the absence of ventral motion cues on the treadmill (N = 29). Left: Acquisition curves as in (A). Right: Heat map as in (A). (C) Data pooled for the two optic-flow conditions and segregated according to the situation in which the CS+ color was Blue while the CS− color was Green. Acquisition curves in terms of the percentage of bees responding to the CS+ (blue), to the CS− (green) or not making any choice (NC; gray) during the ten conditioning trials. The blue, green and gray areas around the curves represent the 95% confidence interval of blue+, green− choices and NC, respectively. (D) Data pooled for the two optic-flow conditions and segregated according to the situation in which the CS+ color was green while the CS− color was blue. Acquisition curves in terms of the percentage of bees responding to the CS+ (green), to the CS− (blue) or not making any choice (NC; gray) during the ten conditioning trials. The green, blue and gray areas around the curves represent the 95% confidence interval of green+, blue− choices and NC, respectively.