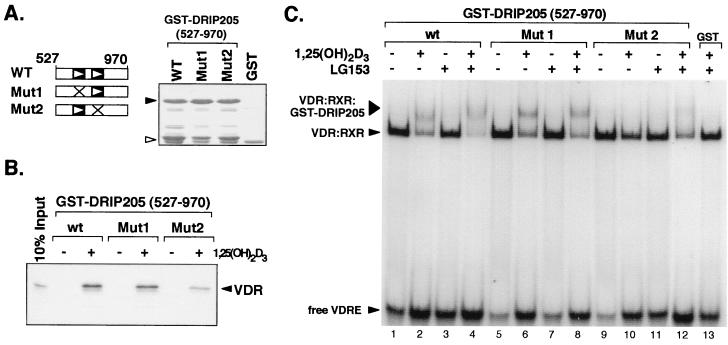
FIG. 5.
DRIP205 binds a VDR-RXR heterodimer on DNA through contributions of both NR boxes. (A) Schematic representation of GST-DRIP205(527-970) wild-type protein (WT), or the same fragment containing point mutations in the NR1 or NR2 box that change each LXXLL motif to LXXAA (Mut1 or Mut2). The GST proteins used in the experiments depicted in panels B and C were quantitated by visualization on a Coomassie blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel (right). Black arrowhead, GST-DRIP205(527-970) proteins; white arrowhead, GST alone. (B) GST pull-down assay of in vitro-translated, [35S]methionine-labeled VDR and GST-DRIP205(527-970) protein fragments. The pull-down assays were carried out in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 10−6 M 1,25(OH)2D3, as indicated, and VDR was visualized by autoradiography. (C) Association of DRIP205 to DNA-bound VDR-RXR heterodimers. Gel mobility shift analysis was performed in the presence of purified VDR, RXR, and GST-DRIP205(527-970), together with a VDRE oligonucleotide as a probe. GST-DRIP205 wild-type (wt), Mut1, and Mut2 proteins (A) were used in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 10−6 M of 1,25(OH)2D3 or LG153 ligands.