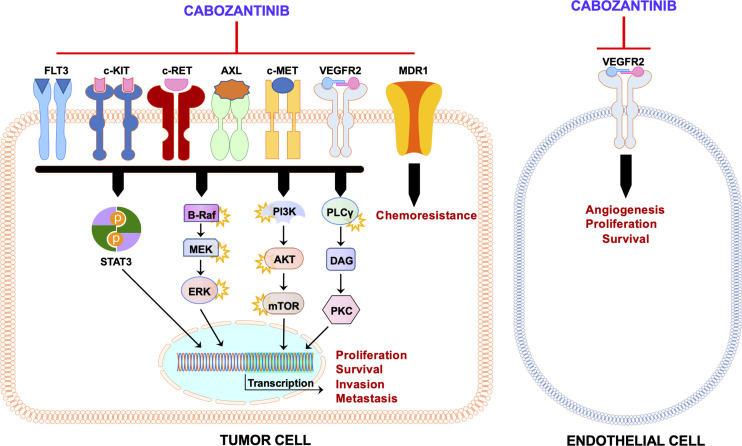
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the mechanism of action of cabozantinib. Administration of cabozantinib to cancer cells leads to the inhibition of several tyrosine kinases (c-MET, VEGFR2, AXL, c-KIT, c-RET, and FLT3) as well as MDR1/P-glycoprotein in the tumor cell and/or in the endothelial cell. These tyrosine kinases, once activated, induce a plethora of downstream pathways (STAT3, Ras/BRAF/MEK/ERK, AKT/mTOR, PLCγ/PKC, etc.) that lead to several biologic effects on the cells (proliferation, survival, migration, chemoresistance, etc.). These activities are blunted by cabozantinib. Black arrows indicate activation, whereas red blunted arrows indicate inhibition.