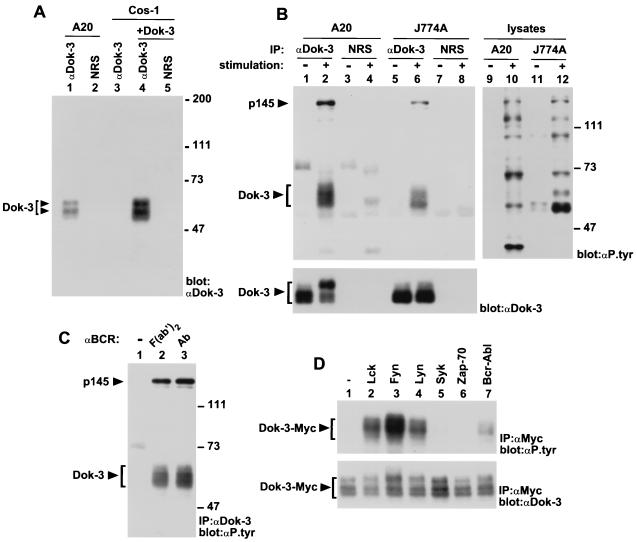
FIG. 3.
Impact of immunoreceptor stimulation on Dok-3 tyrosine phosphorylation. (A) Identification of the Dok-3 protein. The presence of Dok-3 in A20 B-cells and transfected Cos-1 cells was detected by anti-Dok-3 immunoblotting of the indicated immunoprecipitates. The positions of the two forms of Dok-3 are indicated on the left, while those of prestained molecular mass markers are shown on the right. Exposure: 3 h. NRS, normal rabbit serum. (B) Effect of cellular activation on Dok-3 tyrosine phosphorylation. A20 B cells (2 × 107 cells) were activated by incubation for 2.5 min with F(ab′)2 fragments of SAM IgG, while J774A macrophages (1.5 × 107 cells) were activated by stimulation for 2 min with mouse IgG2a (MAb 7G7) and F(ab′)2 fragments of SAM IgG. The positions of Dok-3 and p145 are indicated on the left; those of prestained molecular weight markers are shown on the right. Exposures: top panel, 24 h (lanes 1 to 8) and 48 h (lanes 9 to 12); bottom panel, 14 h. IP, immunoprecipitation. (C) Effect of FcγRIIB coaggregation on BCR-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of Dok-3. A20 cells were treated as for panel B, except that either F(ab′)2 fragments of SAM IgG (lane 2) or intact SAM IgG (Ab; lane 3) was used for stimulation. The locations of Dok-3 and p145 are shown on the left, whereas those of prestained molecular mass markers are indicated on the right. Exposure: 22 h. (D) Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of Dok-3 by various protein tyrosine kinases. Cos-1 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated cDNAs in the presence of a Myc-tagged version of Dok-3. Adequate expression of the PTKs was documented by parallel immunoblotting of total cell lysates with antibodies against these various molecules (data not shown). The migration of Dok-3-Myc is shown on the left. Exposures: top panel, 4 h; bottom panel, 16 h.