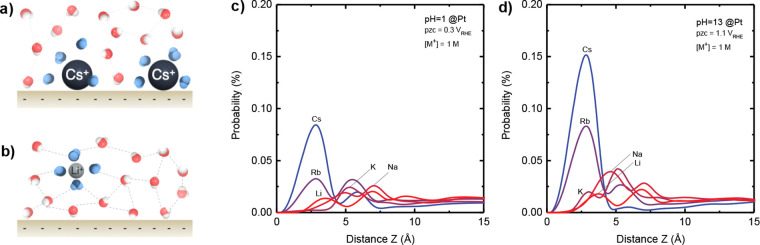
Figure 1.
Tuning the outer Helmholtz layer (OHL) structure at the electrode/electrolyte interface by spectator ions contained in the electrolyte. Schematic illustration showing the interactions among interfacial water molecules, cation, and the interface where (a) water molecules are removed from the interface by larger cations (Cs+) due to strong ion-surface interaction and (b) stable interfacial water layer in the presence of smaller cations (Li+). Strongly H-bonded (ice-like) and asymmetric H-bonded (solvating ion) water molecules are represented in red and blue, respectively. The z-axial probability distribution function (ZDF) of the surface cation in a classical MD simulation of Pt(111) for (c) pH 1 at 0 VRHE, 0.3 V lower than the potential of zero charge (PZC) and (d) pH 13 at 0 VRHE, 1.1 V lower than PZC, where the unit cells contain 2293 water molecules, 42 cations, 42 Cl– anions, corresponding to 1 M cation in water.