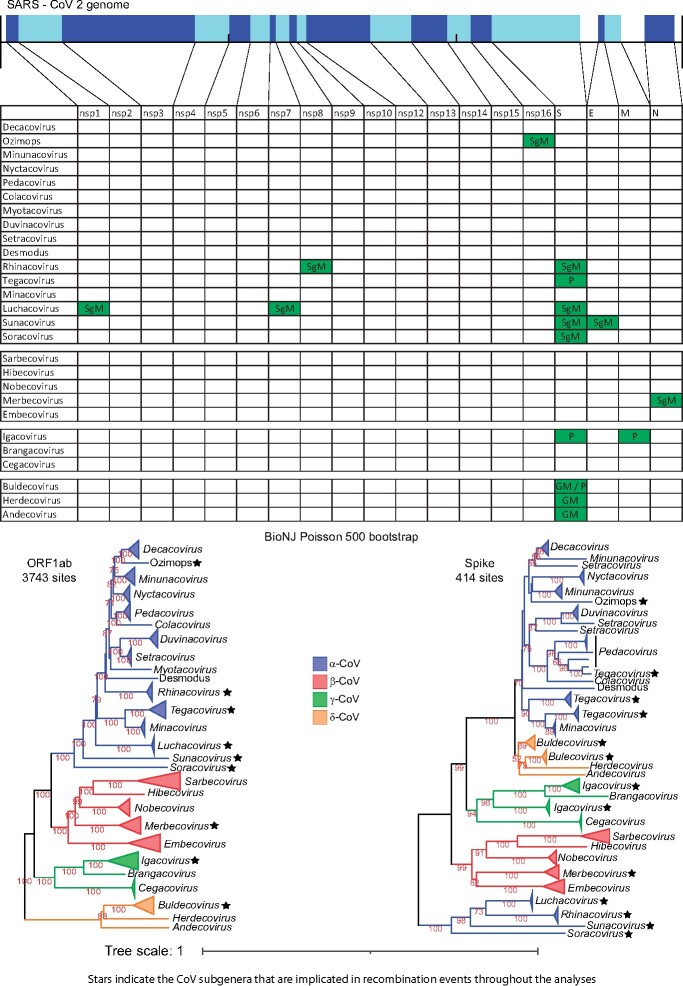
Fig. 2.
The genomic organization of the core ORFs and peptides of the SARS-CoV-2 genome are displayed on the top of the figure. The table/matrix below it shows which genomic regions of the various subgenera are involved in intertypic recombination events. “GM” represents events that occurred at the common ancestor of the genus. “SgM” represents events that occurred at the common ancestor of the subgenus. “P” represents more recent events that occurred for one or few members of the subgenus and have resulted in a polyphyletic tree pattern (for that region and subgenus). All incongruence events in the matrix are supported by the three phylogenetic tree methods (NJ, PhyML, and Bayesian) and are also statistically significant, based on the AU test of CONSEL. Two phylogenetic trees (of ORF1ab and Spike) for all four genera are also included below the matrix, to visualize the recombination events of the Spike region. In these trees, we use stars to denote subgenera that have been involved in intertypic homologous recombination events, in any genomic region (not only the Spike).