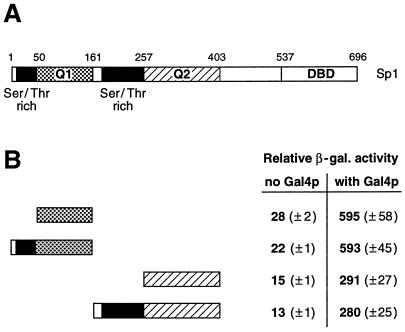
FIG. 4.
The serine/threonine-rich domains of Sp1 do not influence transactivation by the adjacent glutamine-rich activation domains. (A) Schematic drawing of full-length Sp1 transcription factor (696 amino acids). Sp1 harbors two glutamine-rich activation domains termed Q1 and Q2, two serine/threonine-rich domains, and a DBD at the C terminus. (B) Quantitative β-galactosidase assay. The activity of the glutamine-rich activation domains Q1 and Q2 were compared with N-terminal extensions that included the serine/threonine-rich domains. The activity of the different Lex DBD hybrids was assayed in yeast when bound to the proximal position, either alone (no Gal4p) or in combination with a distal Gal4p activator (with Gal4p). The serine/threonine-domain-containing constructs activated reporter gene expression indistinguishably from that of the respective activation domains Q1 or Q2.